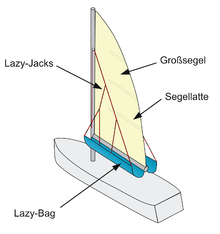
Batten

Sail battens are wooden or plastic strips that are inserted into mostly horizontal pockets on the sail, mostly mainsail , rarely headsail or jib , in order to optimize the shape of the sail and enlarge it beyond the triangular shape.
A distinction is made between short battens, which only stabilize the leech of the sail, and battens that extend right up to the mast, which, especially in the case of main sails of catamarans , regatta ships, junks , and surf sails , open the leech with a given mast and boom length and thus enlarge the sail area. Thus, more and more effective sail area can be used. Restricting the exhibition mostly arise by the backstay . This is why some regatta ships do not have a backstay, but only backstage in order to be able to display the mainsail to the maximum. Profiled battens are often used, which bend more easily at the front than at the back, in order to enable an optimal sail profile.
Limitations for battens result in particular from furling systems . That is why there are constructions with vertical battens in order to achieve a compromise between rollability and stabilization of the leech. There are also so-called roller slats made of spring steel that can be wrapped around the roller system. This enables tri-radial sail cuts and modern designs.