Simonis Chromone Synthesis
The Simonis Chromon Synthesis is a name reaction in organic chemistry. It was discovered in 1913 by chemists Ernst Petschek and Hugo Simonis . It is used for the synthesis of chromone from phenol and a β- keto ester.
Overview reaction
In this P 2 O 5 -catalyzed reaction, phenol and a β-ketoester are cyclized to form chromone:
The reaction can also take place with substituted phenols and other β-ketoesters.
mechanism
The complex mechanism of the Simonis chromone synthesis is still discussed in the literature.
It is assumed that phenol 1 initially attacks oxonium ion 2 from the underside . This leads to the formation of transition state 3 . In a double elimination reaction, water is first split off, creating molecule 4 . After the subsequent elimination of ethanol , 2-methylchromone 5 is formed .
application
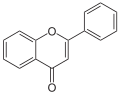
Chromone (1,4-benzopyron) forms the basic skeleton of the flavones (2-phenylchromones) and isoflavones (3-phenylchromones). Isoflavones occur as a yellow dye in some plants and their flowers. The Simonis Chromon Synthesis is used in the production of flavones. Phenol reacts with ethyl benzoylacetate ( enol tautomer) under catalysis by P 2 O 5 to form the natural polymethine dye flavone. In addition, the Simonis chromone synthesis can be used to produce the natural product Visnagin, which is found in some fruits.
See also
Individual evidence
- ^ Organic chemistry . In: Journal of the Chemical Society, Abstracts . tape 104 , no. 0 , 1913, p. i813-i921 (890) , doi : 10.1039 / CA9130400813 .
- ↑ Ernst Petschek, H. Simonis: A new chromone synthesis . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . tape 46 , no. 2 , 1913, pp. 2014–2020 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.191304602117 .
- ↑ a b c d Eberhard Breitmaier, Günther Jung: Organic Chemistry: Fundamentals, Compound Classes, Reactions, Concepts, Molecular Structure, Natural Products, Synthesis Planning, Sustainability Vol. 7. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, 2012, ISBN 978-3-13-541507- 9 , pp. 695-696.
- ↑ a b c d e f Jie Jack Lie, EJ Corey: Name Reactions in Heterocyclic Chemistry II. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, 2011, ISBN 9780470085080 , pp. 479-486, doi 10.1002 / 9781118092828.
- ↑ Martha Windholz, Susan Budavari, Lorraine Y. Stroumtos, Margaret Noether Done: The Merck Index An Encyclopedia of Chemicals and Drugs Vol. 9, Merck & Co., INC., Rahway, NJ, 1976, ISBN 0-911910-26- 3 , p. ONR-82.