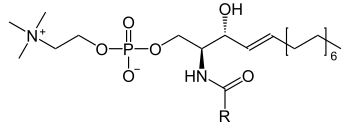
Sphingomyeline

For sphingomyelins, R is z. B. a phosphoethanolamine or phosphocholine group
Sphingomyelins , also called sphingophospholipids , belong to the group of phospholipids and sphingolipids and, like these, are composed of a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails, giving them an amphiphilic character.
The basic structure of the sphingomyeline is sphingosine . A fatty acid is linked to the C 2 amino group via an amide bond and a phosphate group is linked to the C 1 hydroxy group via a phosphoester bond . Analogously to the phosphoglycerides , this phosphate group can be esterified with another alcohol. Prominent examples of these alcohols are ethanolamine or choline . Sphingolipids are building blocks of plasma membranes, and plasma membranes of nerve cells have particularly high concentrations of sphingomyelin (→ myelin sheath ).
Biological function
The essential lipids in the eukaryotic cell membrane include glycerophospholipids , cholesterol and sphingolipids (phospho- and glycosphingolipids). The sphingolipids, the main representative of which is sphingomyelin, make up a percentage of 1–2%.
See also
literature
- Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer : Biochemistry. 6 edition, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2007. ISBN 978-3-8274-1800-5 .
- Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet: Biochemistry. 3rd edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York 2004. ISBN 0-471-19350-X .
- Bruce Alberts , Alexander Johnson, Peter Walter, Julian Lewis, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts: Molecular Biology of the Cell , 5th Edition, Taylor & Francis 2007, ISBN 978-0815341062 .