Split engine
A Split-Cycle Engine (also split Engine ) is a concept for further development of the four-stroke - combustion engine . Instead of a temporal separation of the cycles in each cylinder , the cycles are spatially divided between two cylinders (cylinder pair).
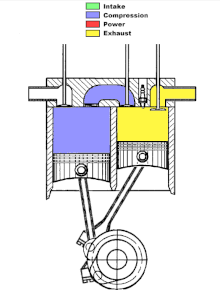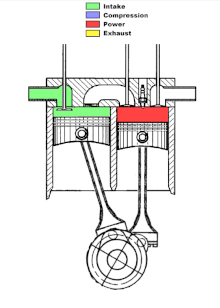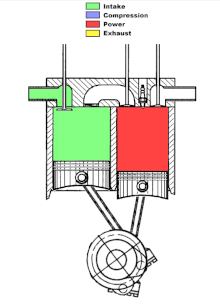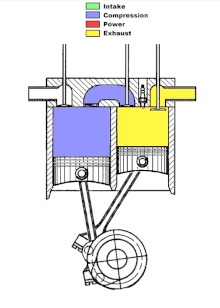
In the first cylinder intake and compression take place, in the other cylinder combustion and exhaust. The air compressed in the compression cylinder is fed into the combustion cylinder through a transfer channel. In the transfer channel or in the compression cylinder, fuel is injected and the fuel-air mixture is ignited in the working cylinder. Due to the local division of the strokes, the stroke cycle engine reaches a lower temperature of the compressed air-gasoline mixture due to the colder compression cylinder. As a result, and because of the ignition after top dead center, a lower working temperature and lower nitrogen oxide emissions are achieved overall.
As with charged direct-injection diesel engines , a split engine should be able to achieve an efficiency of over 40% .
The technology can be expanded into a compressed air hybrid machine without much effort. The compressed air, which is generated in the partial load range of the engine and also when braking , can be stored in a compressed air tank as pre-compressed and pre-cooled charge air.
In March 2008, the Scuderi Group presented the first prototype of its split-cycle engine, the Scuderi engine . Another prototype, in which Bosch Engineering was involved as a development partner for the injection system and engine control, was completed in January 2009, according to the company.
criticism
From a thermodynamic point of view , the delayed ignition causes a deterioration in efficiency. The optimal constant space process cannot be realized. In the transfer pipes there are losses due to air friction and warming that the normal four-stroke engine does not know.
Tour engine
Hugo Tour from Kirjat Gat (Israel) has been working on its own version of an engine with divided clock cycles since 2007 . The left cylinder draws in the cold fuel mixture and compresses it; in the right cylinder it is burned and expelled. The pistons have an offset angle of rotation. At the end of the exhaust stroke, there is no longer any residual gas in the working cylinder. Ignition takes place around 30 °… 50 ° after top dead center of the right cylinder.
There are two prototypes (2008 and 2012) in which two standard engines were combined. Compared to a conventional combustion engine, it should have a 20% higher energy efficiency and emit 30% less nitrogen oxide .
Six stroke
As a variant, there is a three-cylinder engine in which two small pistons take over the gas pre-compression and drive a large central piston.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Scuderi, press release of February 9, 2009 ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Tours prototype (English)
- ↑ Discussion about Tours Motor [1]
- ↑ Tours description (English)