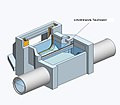
Diving wall
A diving wall is a wall that is immersed in liquids.
functionality
A diving wall represents an obstacle in open water or in an open or closed channel , which is designed in such a way that the flowing medium (e.g. water, waste water, etc.) must flow through under the diving wall. Media or substances that have a lower density than the medium to be transported (water) are generally called floating substances, as these move (swim) on the surface. Examples of this can be wood, oils, fats, fuels (gasoline, etc.) or flotsam. The flowing medium is mostly water. Since the water flows under the diving wall, the floating matter is retained on the surface in front of the diving wall.
field of use
In urban water management, the medium to be transported is mostly sewage or mixed water. In this area in particular, with the help of baffles, ecologically harmful floating matter is kept in the sewer system during relief events and thus not fed into the natural receiving water. These retained floating substances are fed to the sewage treatment plant via the canal. There they can be properly disposed of. In the area of mixed water management, movable baffles are increasingly being used.
Types
Fixed baffles
Fixed baffles are transverse structures, mostly vertical walls in flow cross-sections that are at the water level.
Movable diving walls
The movable baffles include radially movable and also vertically movable baffles. The principle is based on a floating body, which is partly immersed in the water and partly floats on the surface of the water. This creates a barrier on the surface of the water that is able to hold back floating matter. Due to the mobility of this type of diving wall, the diving wall swims continuously with the different water levels, can optimally adapt to the different flow situations and achieve the retention of floating matter.
Vertically floating diving walls
As mentioned above, vertically floating baffles are movable baffles that can only move vertically, i.e. only up or down. They are mostly held horizontally by side guide rails. It is important to ensure that it is guided safely and without tilting, as otherwise no optimal retention of floating matter can be guaranteed.
literature
- W. Bischofberger, W. Hegemann: Lexicon of wastewater technology . 6th edition. 2000