Thioureide
| Thioureide (examples) |
|---|
 Acyclic thioureid |
 Thiouracil ( tautomerism ) cyclic thioureid |
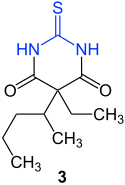 Thiopental (malonic acid derivative) cyclic thioureide |
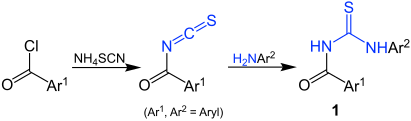
Thioureids are organic chemical substances that are formally derived from thiourea (H 2 N – CS – NH 2 ) and carboxylic acids (R – COOH). Substituted representatives such as Ar – CO – HN – CS – NHR are also called thioureids.
The cyclic thioureids, such as thiouracil ( 2 ) and the drug thiopental ( 3 ), are of particular importance .
According to IUPAC rules C-971.2 and C-974.1, compounds with the atomic grouping -NH-CS-NH 2 are to be referred to as thioureido derivatives in systematic names.
Manufacturing
Thioureids (such as 1 ) are synthetically accessible through the reaction of aromatic carboxylic acid chlorides (Ar 1 COCl) with ammonium thiocyanate and subsequent reaction with an aromatic amine (Ar 2 –NH 2 ):
Thiopental ( 3 ) - the cyclic thioureide of a dialkylated malonic acid - is made from thiourea and a diester of this dialkylated malonic acid.
Individual evidence
- ^ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (editor): Römpps Chemie Lexikon , 8th edition, Frank'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1983, ISBN 3-440-04513-7 , p. 4250.
- ↑ Itamar L. Gonçalves, Rafaela R. da Rosa, Vera L. Eifler-Lima1, Aloir A. Merlo: The use of isoxazoline and isoxazole scaffolding in the design of novel thiourea and amide liquid-crystalline compounds , Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16 , 175-184, pp. 175-184 doi: 10.3762 / bjoc.16.20 .
- ^ Axel Kleemann , Jürgen Engel: Active pharmaceutical ingredients. 2nd edition, Thieme-Verlag, Stuttgart 1982, ISBN 3-13-558402-X , pp. 877-878.