Tibia (arthropod)
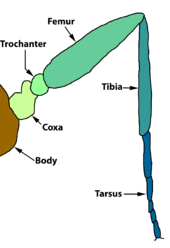
The tibia, or splint, is part of the arthropod's leg .
In the course of evolution , the legs and thus their parts specialized. The extinct trilobites already had many and richly articulated legs, the limbs of which looked largely the same. For legs that specialize in locomotion in the countryside, it is evident that they must have some functional similarities. Part of the leg must ensure safe contact with the ground. Relatively long limbs must allow the body to move further by alternately bending and stretching. The legs must be turned into the body. The insect leg shows a certain analogy to the structure of the human leg, which is why the terms foot, splint (lower leg), thigh (thigh) and hip or their Latin equivalents were obvious. However, the insect legs cannot be homologated with the leg members of vertebrates . Thus the tibia becomes just a name for a particular limb of the arthropod's leg. For example, in the spider bone, the tibia lies between the metatarsus and patella, but all three limbs are identical in structure and function.
literature
- Cedric Gillott: Entomology. 3rd edition. Springer, Dordrecht 2005, ISBN 1-4020-3182-3 .
- Heiko Bellmann : Cosmos Atlas Arachnids of Europe. 2nd Edition. Franckh-Kosmos, Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-440-09071-X .