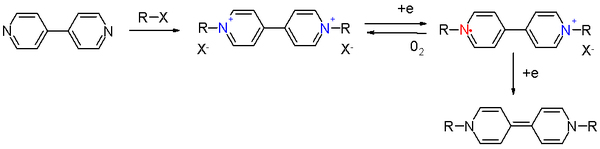
Viologene
The viologens are quaternary 4,4′-bipyridinium salts that show pronounced photochromism . They are converted into intensely colored radicals in a reversible reaction through one-electron transfer. The herbicide paraquat dichloride (methyl viologen), for example, is colorless, whereas the reduction product is deep purple in color. The slight formation of radicals is responsible for the high toxicity of the bipyridinium herbicides.
According to Thomas Arrhenius, elongated electron- conducting , conjugated polyenes with pyridinium end groups are referred to as caroviologs . These can be used as a molecular wire.
Individual evidence
- ↑ entry to Viologens. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on January 20, 2014.
- ↑ TS Arrhenius, M. Blanchard-Desce, Jean-Marie Lehn a . a .: Molecular devices: Caroviologens as an approach to molecular wires - synthesis and incorporation into vesicle membranes. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . 83, 1986, pp. 5355-5359, doi : 10.1073 / pnas.83.15.5355 ( PDF ).