Words (Unix)
words , a standard file on Unix and Unix operating systems , is a simple list of words (dictionary words). This file is used, for example, for automatic spell checking .
Location
The file can usually /usr/share/dict/wordsbe found as , occasionally as /usr/dict/words or /usr/share/lib/dict/words, which can be symbolic links . The concrete situation can look like this, for example:
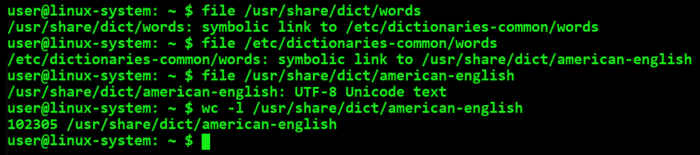
/usr/share/dict/wordsis a symbolic link to /etc/dictionaries-common/words, which in turn is a symbolic link to /usr/share/dict/british-english. The following picture documents such an indirect addressing via several references in an Ubuntu derivative .
Structure of the file
Each word is on its own line. The file is sorted by ASCII values, that is, it begins with a list of words that begin with an uppercase letter (AZ), followed by words that begin with one of the lowercase letters of az, followed by words that begin with Special letters such as ä or é begin; in this last section, too, the words beginning with capital letters are placed before those that begin with lower case letters.
scope
The size of the file varies greatly, even with word lists for the same language.
| scope | year | Filename | source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 230,000 | 2009 | Knaster / Dalrymple | |
| 102305 | 2020 | american-english | Linux Lite 4.8 |
| 98,569 | 2012 | Schwartz, Zaitsev, Tkachenko |
Application and purpose
The file is often used in Unix and Linux books or in programming guides to demonstrate or practice commands that can be used, for example, to search or filter text files.
Programs that work with the words file
- look, a utility program that appeared for the first time in version 7 of AT&T UNIX that searches for words with a certain beginning in this file - optionally without distinguishing between uppercase and lowercase letters.
- xedit, a text editor.
Installation on Linux
Under Debian and Ubuntu , the virtual program package wordlist stands for the file words; packages such as wbritish or wamerican words are actually implemented. Under Fedora and Arch , the file comes onto the system with the words package.
| distribution | Package name | Installation command | Explanations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fedora | words |
yum install words
|
|
| Ubuntu | wordlist |
sudo apt-get install wngermansudo apt-get install wamericansudo apt-get install wbritish
|
wordlistis a virtual package, i.e. not a physical package, but an abstraction, a kind of placeholder for various special packages that fulfill the function of wordlist. The special physically existing package must be installed in each case, for example wngermanor wbritish.
|
In newer Linux distributions based on Debian, including newer Ubuntu versions, you can use apt-getthe newer and shorter command instead of the older command apt.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Shantanu Tushar: Linux Shell Scripting Cookbook . Packt Publishing, Birmingham, UK. 2013, ISBN 978-1-78216-275-9 , pp. 219f (English, [1] ).
- ↑ Harley Hahn: Harley Hahn's Guide to Unix and Linux . McGraw-Hill Education, 2008, ISBN 978-0-07-313361-4 , pp. 515 .
- ^ Emmett Dulaney: Novell Certified Linux Professional (Novell CLP) Study Guide . Novell, Indianapolis 2005, ISBN 0-672-32719-8 (English).
- ^ Arnold Robbins: Effective awk Programming: Universal Text Processing and Pattern Matching . 4th edition. O'Reilly, 2015, ISBN 978-1-4919-0496-1 (English).
- ^ Baron Schwartz, Peter Zaitsev, Vadim Tkachenko: High Performance MySQL: Optimization, Backups, and Replication . 3. Edition. O'Reilly, Sebastopol 2012, ISBN 978-1-4493-1428-6 , pp. 156 (English): "[...] To illustrate this, we loaded all the words in / usr / share / dict / words into a table along with their CRC32 () values, resulting in 98.569 rows."