Tooth fracture
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| S02.5 | Tooth fracture |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
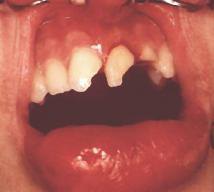
A tooth fracture ( lat. Fractura "break") is a break, a split, a splintering or even just a crack (infracture) of a tooth , which is caused by traumatic impact, which is caused by a shock or impact (mostly in the anterior tooth area - see also Anterior tooth trauma ), a bite on a hard foreign body in food, a so-called shotgun fracture (for example, a bite on a shotgun in venison, on a cherry stone or an unground grain in whole grain products ), an accident or during a tooth extraction ( extraction ).
Tooth fractures can also occur in milk teeth .
Systematics and therapy
A distinction is made depending on the location of the break:
- Fracture in the area of the tooth crown
- divided into:
- Fracture exclusively in tooth enamel; Therapy : filling or crown
- Fracture in the tooth enamel and dentin without involvement of the pulp (tooth nerve); Therapy: indirect capping ; then filling or crown
- Fracture in tooth enamel and dentin with involvement of the pulp; Therapy: direct pulp capping or pulpotomy (removal of the vital pulp in the tooth crown) or vital extirpation (removal of the vital pulp to the root tip); then filling or crown
- Fracture at the level of the tooth neck ; Therapy: root canal treatment ; then post build-up or post crown
- Tooth root fracture
- divided into:
- Fracture in the upper third of the root; Therapy: root canal treatment ; then post build-up or post crown
- Fracture in the middle third of the root; Therapy: extraction
- Fracture in the lower third of the root; Therapy: apicectomy
- Longitudinal fracture; Therapy: extraction
Illustrations
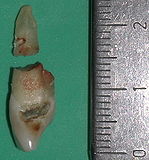
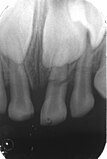
Transverse fracture in the middle third of the root of a lateral upper incisor; Secondary finding: deep caries on the fractured tooth
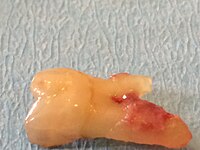
Transverse fracture in the middle third of the root; Secondary finding: approximal caries
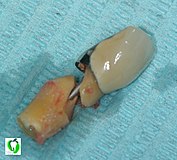
Fracture of a removed tooth in the area of the tooth neck that was previously restored with a post crown. The tooth had previously been resected ( root tip resection ).
See also
- tooth
- Dental crown
- Tooth root
- Root canal treatment
- Extraction (dentistry)
- Evaluation standard of dental services
swell
- Walter Hoffmann-Axthelm : Lexicon of Dentistry , Quintessenz-Verlag, Berlin
- Dental knowledge lexicon, keyword "tooth fracture"