COVID-19 pandemic in Brandenburg
The COVID-19 pandemic occurs in Brandenburg since 2020 as part of the global COVID-19 pandemic and in particular the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany on. The pandemic affects the novel disease COVID-19 . This is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus from the Coronaviridae group and belongs to the group of respiratory diseases .
On March 3, 2020, an infection that tested positive for the coronavirus was confirmed for the first time in Brandenburg. The person returned from South Tyrol to the Oberhavel district . According to the Robert Koch Institute , parts of northern Italy have been a COVID-19 risk area since February 27, 2020 . From March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) classified the outbreak of the novel coronavirus as a global pandemic .
statistics
Cases of infection
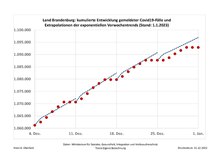
Confirmed infections (cumulative) in Brandenburg
(based on data from the RKI from the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany )

- The negative values are due to reporting errors and corrections.
Confirmed infections (new cases) in Brandenburg
(based on data from the RKI from the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany )

Deaths
Confirmed deaths (cumulative) in Brandenburg
(based on data from the RKI from the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany )

Confirmed deaths (daily) in Brandenburg
(based on data from the RKI from the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany )

Remarks
- ↑ a b c d This is a list of cases that were reported to the RKI via the reporting channel or official sources. Since the situation is very dynamic, there may be deviations or delays between the RKI cases and information from other bodies, such as the federal states concerned or the World Health Organization (WHO).
- ↑ a b c d For June 14, 2020, the RKI announced: "Baden-Württemberg, Brandenburg and Hamburg did not transmit any data over the weekend."
Reactions and actions
On March 12, the state government instructed the districts to issue general orders banning major events and forbidding returnees from certain risk areas from entering public facilities.
With an ordinance on March 17, 2020, the state of Brandenburg banned public traffic in sports, leisure and amusement facilities, restricted visitors to clinics, old people's and nursing homes and prohibited the operation of facilities for the disabled, with the exception of emergency care there.
From March 18, Brandenburg decreed a state-wide school closure. Emergency care was subsequently set up for children whose parents work in systemically important professions.
This regulation was replaced by another on March 23, 2020. In addition to the nationwide ban on contact, the state government issued a "ban on entering public places such as paths, streets, squares and parks". Numerous exceptions were defined such as work, necessary shopping, child care and individual outdoor sports.
On April 9, 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 Quarantine Ordinance (SARS-CoV-2-QuarV) was also issued, which stipulates a fourteen-day quarantine for incoming and outgoing travelers. It is initially valid until April 19, 2020.
Since Brandenburg is an areal state, the positive test numbers and deaths have long been well below the national average. At the end of March and beginning of April, however , more than 100 of the 2,300 employees in the Ernst von Bergmann Potsdam Clinic were infected with the virus. Patients were also infected in large numbers. By April 14th, 24 people with a positive corona test had died in the clinic - more than half of a total of 40 fatalities during this time. It was particularly problematic that the geriatric department was not strictly isolated and the patient's routes through different departments of the clinic could no longer be traced. The public prosecutor is investigating investigations against three senior doctors and the two managing directors of the clinic. Due to the grievances, it was decided to restructure the clinic areas into three strictly separated areas: a black area with patients who tested positive for Corona, white for patients who tested negative and gray for patients with outstanding results. By April 16, the number of people who died in the clinic rose to 36, with 54 dead in the country. Since the clinic did not provide the state government with the information requested about the infections after repeated requests, the clinic is now threatened with a fine. After two weeks, the clinic presented data on April 16, which, however, was warned as incomplete. The illnesses also affected the psychiatric clinic several kilometers from the main building.
On April 15, the Brandenburg State Parliament passed an emergency law that allows local parlors - district assemblies and local councils - to meet via video and telephone conferences
By April 16, emergency aid of 740 million euros had been made available by the state government.
Potsdam was the first city in Brandenburg to announce a mask requirement from April 27, 2020 . The Brandenburg Health Minister Ursula Nonnemacher spoke out on April 21st against a mask requirement. Just three days later, however, the cabinet passed such an obligation in public transport and in shops from April 27th.
See also
Web links
- Robert Koch Institute, University of Bonn - Institute for Hygiene and Public Health, ESRI : Robert Koch Institute: COVID-19 Dashboard . (RKI data at state and district level).
Individual evidence
- ↑ Pulmonologists on the net: Covid-19: Causes . Online at www.lungenaerzte-im-netz.de. Retrieved April 4, 2020.
- ^ First corona case in Brandenburg. Ministry of Social Affairs, Health, Integration and Consumer Protection of the State of Brandenburg (MSGIV), March 2, 2020, accessed on April 4, 2020 .
- ↑ Robert Koch Institute (Ed.): COVID-19 (Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2): Risk areas , as of February 27, 2020. Published on the RKI website. ( Memento in archive.org )
- ↑ Tagesschau: "Deeply worried". WHO speaks of corona pandemic . March 11, 2020. Online at www.tagesschau.de. Retrieved April 4, 2020.
- ↑ Press release of the Oberhavel district of March 12, 2020. Oberhavel district, March 12, 2020, accessed on April 9, 2020 .
- ↑ Ordinance on measures to contain the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in Brandenburg. (PDF) Ministry of Justice of the State of Brandenburg, March 17, 2020, accessed on March 30, 2020 .
- ↑ Ordinance on measures to contain the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in Brandenburg. (PDF) Ministry of Justice of the State of Brandenburg, March 22, 2020, accessed on March 30, 2020 .
- ↑ SARS-CoV-2 Quarantine Ordinance. (PDF) State government of Brandenburg, April 9, 2020, accessed on April 9, 2020 .
- ↑ Ulrich Thiessen: Coronavirus: Potsdamer Klinikum becomes a problem case. April 9, 2020, accessed April 16, 2020 .
- ^ Proceedings initiated against doctors at the Bergmann Clinic in Potsdam. Retrieved April 16, 2020 .
- ^ Dpa: Corona pandemic: Bergmann Clinic in Potsdam gets three new clinic areas. April 14, 2020, accessed April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ dpa: Corona crisis: Potsdam requests data from the Bergmann Clinic and threatens a fine. April 16, 2020, accessed April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ Bergmann-Klinikum presents corona list - but it is incomplete. Retrieved April 16, 2020 .
- ^ Pandemic in Potsdam unchecked. Retrieved April 16, 2020 .
- ^ Dpa: Corona crisis: Large majority in the state parliament for municipal emergency law. April 15, 2020, accessed April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ dpa: Financing: So far, 740 million euros Corona aid for Brandenburg. April 16, 2020, accessed April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ From next week, mask compulsory in Potsdam! In: bz-berlin.de. Accessed June 1, 2020 .
- ↑ Potsdam is planning to wear a mask from next week. In: rbb24.de. Accessed June 1, 2020 .
- ↑ Brandenburg introduces mask duty, playgrounds stay. In: rbb24.de. Accessed June 1, 2020 .