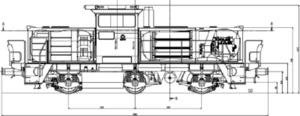
Alstom Prima H3
| Alstom Prima H3 | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer: | ALSTOM Stendal |
| Year of construction (s): | from 2013 |
| Axis formula : | A 'A' A ' |
| Gauge : | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ) |
| Length: | 12,800 mm |
| Width: | 3,130 mm |
| Friction mass: | 67.5 t |
| Wheel set mass : | 22.5 t |
| Top speed: | 100 km / h |
| Starting tractive effort: | 240 kN |
| Tank capacity: | 2200 l |
The Alstom Prima H3 , also known as Prima H3 or Alstom H3 called, is one of ALSTOM Stendal developed shunting - hybrid locomotive .
history
In 2004, Alstom began developing a hybrid locomotive. A locomotive series of the DR series V 100 as series 203.7 served as a test vehicle, eleven of which were built. The conversion was carried out by ALS - ALSTOM Lokomotiven Service GmbH, Stendal, according to the “BR 203.7” conversion concept (hybrid locomotive). The H3 concept was presented at Innotrans 2012.
In August 2013, Deutsche Bahn AG ordered five prototypes of this locomotive. The project was an initiative of Eco Rail Innovation and was supported with € 600,000 in funding from the State of Bavaria. It should prove the technical and economic readiness for series production of a diesel locomotive with hybrid drive in daily use in shunting service. The first locomotive was handed over to Deutsche Bahn during Innotrans 2014.
Constructive features
The H3 is designed for shunting and light road service . The vehicle has a center driver's cab and three individually mounted axles, each of which is individually driven by an asynchronous drive motor. The axles are designed as a hydraulic wheel set coupling with passive radial adjustment, which means that when the first axle is screwed into the track curve, the third axle also turns so that the vehicle can drive through very small track curves with little friction. This reduces noise emissions and protects the infrastructure of the route network. The vehicle platform was completely redeveloped by ALSTOM Stendal .
Motorization variants
The engine is offered in four variants:
- A diesel engine with a 1000 kW generator
- Hybrid variant with diesel engine and battery, 350 kW generator. Complies with emissions standard 3b.
- Two diesel engines with two 350 kW generators
- Battery locomotive with 600 kW power
Nickel-cadmium accumulators with a nominal capacity of 170 ampere-hours and a nominal voltage of 600 V were used as batteries . The battery increased the vehicle mass by 6.5 tons. This solution was used for the first locomotives produced because it had proven itself in the test vehicle. New H3s have been equipped with lithium-ion batteries since 2019 . The hybrid variant is said to save 50% fuel and 70% emissions compared to conventional engines.
Awards
For the development of the H3 hybrid shunting locomotive, Alstom Transport Germany was awarded the Privatbahn Magazin innovation prize in 2014/2015 .
commitment
The first prototypes were in use in 2014. The use of the series locomotives began in 2015.
The Volkswagen plant in Wolfsburg received the third locomotive for factory traffic in 2015.
Audi in Ingolstadt got two locomotives in 2015/2016.
The German equipment leasing has ordered nine vehicles. The first five will be used as ALS class 1002 by DB Regio at the Würzburg and Nuremberg locations. In July 2017 the 1002 007 and 008 were used in Nürnberg Hbf . In contrast to the data sheet, these locomotives have a top speed of 60 km / h.
Another four went to the logistics service provider Chemion in 2017 and will be used in the CHEMPARK locations in Leverkusen, Dormagen and Krefeld-Uerdingen.
SBB Cargo has been using the two locomotives 022-4 and 023-2 since summer 2017. They will be tested for two years in the ports of Birsfelden and Kleinhüningen . In January 2018, the 025-7 was added as the third locomotive. It is in action in Wildegg , where it is active in shunting heavy trains with excavated material to the cement works.
In September 2018, MEG received three locomotives, with two more to follow in 2019.
In October 2018, SBB Cargo announced that it was purchasing 12 more locomotives. Alstom produces the hybrid locomotives and SBB Cargo will lease them from Lok Roll 2 AG for the next ten years. The H3 hybrid locomotives will be delivered from October 2020.
photos
Web links
- eb - Electric railways. 1/2013 p. 11 f.
- Alstom manufacturer website : H3, a modular platform for shunting locomotives.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Project start for shunting locomotive fleet with hybrid technology ( Memento from September 26, 2013 in the web archive archive.today )
- ↑ ecorailinnovation.com
- ^ Max Wittwer: SBB Aem 940 locomotive. In: https://www.ews.tu-berlin.de . May 9, 2016, accessed August 19, 2020 .
- ↑ Marcus Hoffmann, Holger Dittus, Johannes Pagenkopf, Mathias Böhm: Alternative drive concepts for shunting and construction vehicles. Preliminary study by SBB. In: https://elib.dlr.de/ . German Aerospace Center - Institute for Vehicle Concepts, March 18, 2015, accessed on April 22, 2020 .
- ↑ Norbert Stirken: Henkelhausen equips hybrid shunting locomotive. In: https://rp-online.de/ . RP Digital GmbH, December 18, 2019, accessed on April 22, 2020 .
- ↑ railway magazine . No. 9 , 2015, p. 28 .
- ↑ Also ... In: eisenbahn-magazin . No. 4 , 2015, p. 23 .
- ↑ Hybrid locomotives from DB Regio Franken maneuver quietly and environmentally friendly. (No longer available online.) In: RegioAktuell. DB Regio AG, November 2016, archived from the original on December 5, 2016 ; Retrieved December 5, 2016 .
- ↑ Four Prima H3 hybrid locomotives in use . In: railway magazine . No. 6 , 2017, p. 31 .
- ↑ New H3 shunting locomotives from Alstom in use at SBB Cargo. In: Bahnonline.ch. December 27, 2017. Retrieved September 17, 2018 .
- ↑ Prima H-3 shunting locomotives for MEG . In: railway magazine . No. 12 , 2018, ISSN 0342-1902 , p. 35 .
- ↑ SBB Cargo is expanding its rolling stock portfolio with 12 Prima H3 hybrid locomotives. In: Bahnonline.ch. October 25, 2018, accessed October 27, 2018 .