Amphlet Islands
| Amphlet Islands | ||
|---|---|---|
| NASA satellite image of the Amphlett Islands | ||
| Waters | Solomon Lake | |
| Geographical location | 9 ° 15 ′ S , 150 ° 50 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| Number of islands | 18th | |
| Main island | Gumawana | |
| Total land area | 25 km² | |
| Residents | 469 (2000) | |
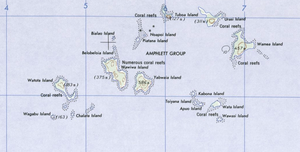
| Map section of the Amphlett Group | ||
The Amphlett Islands are a group of islands in the Solomon Sea . Politically, the islands belong to the Dobu Rural LLG (Local Level Government) Area in the Esa'Ala district of Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea . The group, which in some sources is also considered part of the D'Entrecasteaux Islands , consists of 18 islands and is located about 10 km north of Fergusson Island .
description
The Amphlett Islands are of volcanic origin. The most important islands in the group are: the main island Gumawana (Dobu: Urasi), Wamea (Omeya, Dum Dum), Nabwageta or Tuboa, Wawiwa (also Koyaui, Kwatoita or Kotoita) and Yabwaia or Bituma.
According to the 2000 census, the population of the Amphlett Islands was 469, spread over the three inhabited islands in the northeast of the group, Nabwageta (173), Gumawana (154) and Wamea (142). In 1970 there were 240 people; In addition, the islands of Wawiwa and Yabwaia were inhabited, the two largest islands in the southwest of the group.
The residents are known for their pottery products. They pick up the clay from Wapolu on Fergusson Island , which is a day's trip by canoe away. Pottery production on the Amphlett Islands began 1000 years ago. For about 500 years there has been a monopoly on trade in the entire region, which arose from the kula ritual exchange system .
Island overview
![]() Map with all coordinates: OSM | WikiMap
Map with all coordinates: OSM | WikiMap
history
The D'Entrecasteaux Islands have probably been around since around 1500 BC. Inhabited by Polynesians. They were discovered with the Trobriand Islands in 1793 by Captain Joseph Bruny d'Entrecasteaux in search of Jean-François de La Pérouse . In 1873 and 1874 the British captain John Moresby explored and charted the Amphlett Islands with the ship HMS Basilisk . From 1914 to 1916 and from 1917 to 1918, the anthropologist Bronisław Malinowski carried out studies on the population of the islands and described them in detail in his 1922 book Argonauts of the Western Pacific . The Amphlett Islands were occupied by Japan from 1942 to 1943 .
Web links
- Amphlett Group, Oceandots.com (further information & pictures) ( Memento from December 23, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) (engl.)
literature
- Peter K. Lauer: Amphlett Islands Pottery Trade and the Kula . In: Mankind (The Australian Journal of Anthropology, TAJA) . Vol. 7, No. 3 , 1970, p. 165-176 , doi : 10.1111 / j.1835-9310.1970.tb00403.x .
- Bronislaw Malinowski : Argonauts of the western Pacific . Syndicate, Frankfurt am Main 1979, ISBN 3-8108-0068-6 . (Original title: Argonauts of the Western Pacific , 1922)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Amphlett Group, Oceandots.com ( Memento of 23 September 2012 at the Internet Archive )
- ^ A b c Peter K. Lauer: Amphlett Islands Pottery Trade and the Kula. Mankind (The Australian Journal of Anthropology, TAJA). 1970, Vol. 7 No. 3, pp. 165-176.
- ^ Ethnologue: Dobu, A language of Papua New Guinea
- ↑ http://coombs.anu.edu.au/SpecialProj/PNG/GMAP/census2000/milnebay/esaala.xml ( Memento from July 5, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Arthur Wichman: (Ed.): History of discovery of New Guinea (until 1828). Vol. 1, EJ Brill, Leiden 1909, p. 184