Analog signature analysis
The analog signature analysis (ASA) is a test procedure from electronics production and repair that is often part of an ICT test system .
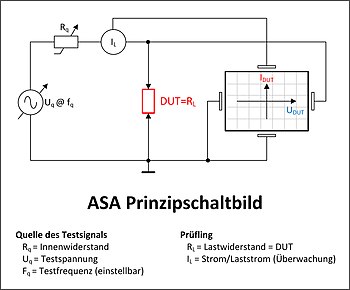
The test is carried out in a voltage-free state on the fully assembled circuit board . Here, current-voltage characteristics ( signature ) are recorded between two measuring points on the circuit board and compared with a reference characteristic. This means that defective (suspicious) assemblies can be identified even before commissioning takes place.
To record the signature, a mixed voltage , i.e. a direct voltage superimposed with alternating voltage , is fed into the test object. There is also a current limitation to avoid overloading. Frequency , voltage, impedance and current limitation can be configured in the test system to match the test path.
Depending on the component , there are different characteristics: A resistor forms a straight line, capacitors have an ellipse and diodes have a kink in the characteristic curve. Since several components are usually connected to one measuring point, the signature actually measured corresponds to an overlay of the individual component characteristics. Some test systems can also measure transistors and other active components via additional measuring points .
Web links
- Information from a manufacturer (Huntron) (PDF; 2.2 MB)
- Information from a manufacturer (Polar Instruments) (PDF; 2.5 MB)
- Article on the use of analog signature analysis in troubleshooting (PDF; 689 kB; accessed August 16, 2018)