Use case diagram
| Structure diagrams of the UML |
|---|
| Class diagram |
| Component diagram |
| Composition structure diagram |
| Object diagram |
| Package diagram |
| Profile diagram |
| Distribution diagram |
| UML behavioral diagrams |
| Activity diagram |
| Use case diagram |
| Interaction overview diagram |
| Communication diagram |
| Sequence diagram |
| Timing diagram |
| State diagram |
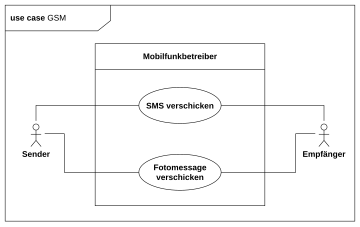
A use case diagram (. Engl use case diagram ), also Nutzfalldiagramm , is one of the types of diagrams of the Unified Modeling Language (UML), a language for the modeling of the structures and the behavior of software - and other systems. It depicts use cases and actors with their respective dependencies and relationships .
The use case diagram has been a behavior diagram since UML 2 . It represents the expected behavior of a system and is therefore used to specify the requirements for a system.
A use case diagram does not represent a process description. Instead, it can be represented with an activity , sequence or collaboration diagram (from UML 2.x communication diagram).
Use case diagram in bullet points
- The aim is to show as simply as possible what you want to do with the software system to be built and which cases of application exist.
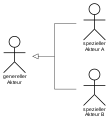
- Actors are represented as " stick figures ", which can represent both people such as customers or administrators and a system (a ribbon symbol is sometimes used in systems).
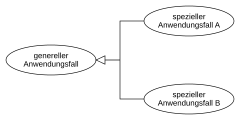
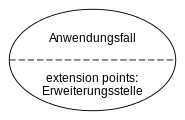
- Use cases are shown in ellipses. They must be described (e.g. in a comment or a separate file).
- Associations between actors and use cases must be indicated by lines.
- System boundaries are indicated by rectangles.
- Include relationships are marked with a dashed line (marked with <<include>> ) and an arrow to the included use case, which is necessary for the calling use case.
- extend relationships are identified by a dashed line (marked with <<extend>> ) and an arrow from the extending use case, whereby this can be activated by the calling use case , but does not have to.
elements
Relationships
Multiplicity of actor and use case, whereby the default setting of the actor is 1.
Examples
A more complex use case diagram that captures the relationships between the actor
Benutzerand the systemMultimediasystem. A user is interested in four use cases, which in turn are related to each other.Musik-CD erstellenis the most complex use case because it imports two other use cases and is optionally extended by a thirdCD beschriften,,.
Differences to UML 1.x
The use case diagram is now classified in UML2 as a behavior diagram and no longer as a structure diagram. Furthermore, actors must now have a name and the preconditions of the respective extension points must be attached to the corresponding extension relationship by means of a note.
See also
literature
- Bernd Oestereich : Analysis and Design with UML 2 , Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag, 2006, ISBN 3-486-57926-6
- Christoph Kecher: UML 2.0 - The Comprehensive Manual , Galileo Computing, 2006, ISBN 3-89842-738-2