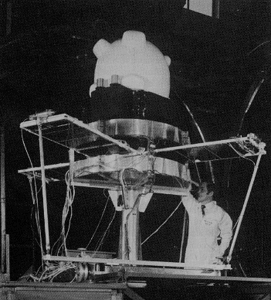
Ariel VI
| Ariel VI | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Country: |
|
| Operator: | SRC / NASA |
| COSPAR-ID : | 1979-047A |
| Mission dates | |
| Dimensions: | 154 kg |
| Begin: | June 2, 1979, 23:26 UTC |
| Starting place: | Wallops Flight Facility LA3A |
| Launcher: | Scout D1 |
| Status: | burned up on September 23, 1990 |
| Orbit data | |
| Rotation time : | 92.1 min |
| Orbit inclination : | 55 ° |
| Apogee height : | 383 km |
| Perigee height : | 372 km |
Ariel VI was a British-American X-ray satellite developed in collaboration between the British SRC and NASA .
Ariel VI (called UK6 before launch) was launched on a Scout missile from the Wallops Flight Facility on June 2, 1979 and was in service until February 1982. The satellite burned up on September 23, 1990 when it re-entered the earth's atmosphere.
Ariel VI had two experiments on X-ray astronomy at energies between 0.25 and 50 keV and one experiment on researching cosmic rays . Due to technical problems - the attitude control system was disturbed by radar on the ground - was Ariel VI scientifically much less successful than its predecessor Ariel V .
Web links
- NASA: Ariel VI (English)
- Ariel in the Encyclopedia Astronautica (English)