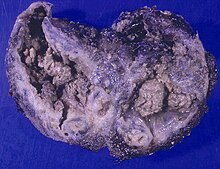
Aspergilloma
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| B44 | Aspergillosis |
| B44.0 | Invasive aspergillosis of the lungs |
| B44.2 | Aspergillosis of the tonsils |
| B44.8 | Other forms of aspergillosis |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
An aspergilloma ( syn. Aspergillus mycetoma) is the colonized form of aspergillosis ( mold infection) that can occur in various locations.
to form
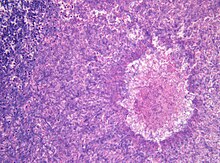
Hematoxylin-eosin stain . Magnification 200x
Aspergilloma of the paranasal sinuses
Typically only one side is affected. The aspergilloma grows non-invasively in the sinuses . It can go undetected for a long time, initial discomfort can be purulent secretion , nosebleeds or a feeling of pressure on the affected side. In the X-ray image , the aspergilloma shows up as a shadowing of the respective paranasal sinuses.
Zinc oxide has proven to promote growth . Since the tips of the roots of the teeth in the upper jaw have a close positional relationship to the maxillary sinus , root filling material, which contains zinc oxide-eugenol, can get into the paranasal sinus as part of an endodontic treatment.
The therapy involves surgical removal of the aspergilloma while protecting the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus. This is done endoscopically through the nose if possible . The aspergilloma appears as a greenish-black stone, which consists of necrotic fungal masses and metabolized calcium . Long-term consequences are not to be expected.
Aspergilloma of the lungs
An aspergilloma can also form in the lungs in existing (preformed) cavities, such as infected pulmonary emphysema bladders or in scar tissue following inflammation (e.g. tuberculosis ). It has a typical X-ray finding, whereby the round aspergilloma moves in the cavity depending on the position of the body. This finding is used to secure the diagnosis.
Furthermore, laboratory values in the blood are increased (total IgE , radio-allergo-sorbent test (RAST for aspergillus, type I and III serology)). Sometimes the aspergillus can be obtained from the bronchial system by means of bronchoscopy . Complications are the continued infection of the cavity with bacteria and especially the life-threatening bleeding from the cavity wall via the bronchi into the whole lungs. The patient suffers from coughing up blood. This is the point in time for the surgical removal of the lung lobe in which the cavity with the aspergilloma is located. Then the patient is cured. A more recent method is intensive intravenous therapy with one of the newer and more expensive antifungal agents (antifungal agents ), especially if no bleeding has occurred or the patient is not fit for surgery.
literature
- JP Latge: Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis . In: Clin. Microbiol. Rev. Vol. 12 (1999), pp. 310-350. PMID 10194462
Individual evidence
- ↑ Norbert Schwenzer, Michael Ehrenfeld: Tooth-mouth-jaw medicine. Volume 1: General Surgery. Thieme, Stuttgart 2000, ISBN 3-13-593403-9 . (Full text)