Assimineidae
| Assimineidae | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
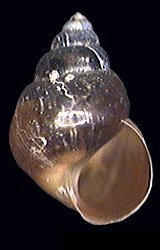
Cone marsh snail ( Assiminea grayana ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Assimineidae | ||||||||||||
| H. Adams & A. Adams , 1856 |
The Assimineidae are a family of snails from the order Sorbeoconcha of the Caenogastropoda . The species in the family live in salt water, brackish water, fresh water or on land. The Acmella nana , published in November 2015, is currently the smallest snail living on land.
features
The moderately large to small cases are conical, more or less high, or ovoid-conical to almost planispiral. The turns are flattened to well arched. The mouth is rounded to ovoid and mostly angled at the top. The edge of the mouth is usually simple, rarely z. T. lipped reinforced. The cap is usually horny, rarely bare and has only a few turns. The nucleus is eccentric. The animals have a short snout and the gill is often reduced. The head tentacles are short or reduced. The marginal tooth of the radula is very wide. The fallopian gland is thickened ventrally, i. H. a ventral longitudinal canal is missing. There is no special ladder for the sperm library. The penis is usually simple, but special glands or attachments can occur.
Geographical distribution and habitat
The species of the family live mainly in the tropics and subtropics, a few species also penetrate into the temperate zones. Most species live in the coastal area, at the edge of lakes, rarely completely terrestrial, in salt water, brackish water, fresh water or on land. The Assimineidae are almost exclusively herbivores or graze on encrusting organisms from plants and mud.
Taxonomy and systematics
The taxon was established in 1856 by Henry Adams and Arthur Adams as the family Assiminiidae, based on the misspelling Assiminia Fleming, 1828. Currently the family is divided into three subfamilies:
-
Assimineinae Fleming; 1828
- Cone marsh snail ( Assiminea grayana )
-
Ekadantinae Thiele, 1929
- Acmella nana Vermeulen, Liew & Schilthuizen, 2015
- Omphalotropidinae Thiele, 1927
The Assimineidae are probably the closest relatives of the sea snails (Hydrobiidae). However, the monophyly is not supported by molecular genetic data.
supporting documents
literature
- Wilhelm Wenz: Gastropoda. Part I: General Part and Prosobranchia. In: Handbuch der Paläozoologie. Volume 6, Verlag der Gebrüder Borntraeger, Berlin 1938, p. 631.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Jaap J. Vermeulen, Thor-Seng Liew, Menno Schilthuizen: Additions to the knowledge of the land snails of Sabah (Malaysia, Borneo), including 48 new species. ZooKeys 531: 1-139 (Nov 2, 2015) doi : 10.3897 / zookeys.531.6097
- ^ Henry Adams, Arthur Adams: The genera of recent Mollusca: arranged according to their organization. Volume II. John van Voorst, London 1856 Online at www.biodiversitylibrary.org (p. 314)
- ↑ Thomas Wilke, Martin Haase, Robert Hershler, Hsiu-Ping Liu, Bernhard Misof, Winston Ponder: Pushing short DNA fragments to the limit: Phylogenetic relationships of 'hydrobioid' gastropods (Caenogastropoda: Rissooidea). In: Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 66 (3), 2013, pp. 715-736 doi : 10.1016 / j.ympev.2012.10.025 .