Seating
Seating refers to the arrangement of chairs in a room. Less often the term describes furnishing a room with chairs.
Functions
In addition to seating with or without a backrest and / or armrest, seating can also have other functions: storage areas such as foldable tables or cup holders can be built into the backrest or armrest. The life jackets are also kept in the seating on airplanes and ferries . In addition, a seating arrangement can contain light sources, electrical outlets and information and entertainment systems. Numbered seating allows the allocation of fixed seats.
Subtitles in the seats of an opera house
Seating types
In principle, seating types in
be divided.
The seating can be firmly anchored in the floor or loose.
A distinction is made between the following types of seating:
Theater seating
The theater seating (also row seating or cinema seating ) comes from the theater and is also used today mainly in the cinema and for lectures. The chairs are set up side by side in rows opposite the stage, screen or podium. For a better view, the rows of chairs can be offset from one another so that each participant can look forward between the heads of those sitting in front of them. For a better view on the sides, the rows of chairs can also be arranged slightly curved to completely circular. There are no tables. Fixed and movable grandstands in sports facilities also fall under theater seating. The high capacity of the room to be seated in relation to other types of seating depends to a large extent on the distance between the seats; the space requirement is approx.
Rows of seats in a small cinema in Yokohama
View of the parquet seating in the Vienna State Opera
Concentrically arranged rows of seats in the Greek theater of Epidaurus
A special form is the herringbone seating , in which the rows are bent in the middle.
Parliamentary seating
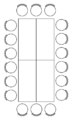
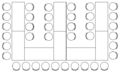
The parliamentary seating (or classroom seating ) differs from the theater seating in that the participants sit at long tables. This allows you to work with table templates or to put down food and drinks or table microphones. The space requirement is about 2 m² per person.
Interactions between the participants are more difficult with this type of seating.
Banquet seating
With banquet seating (also restaurant seating or gala seating ), the participants sit in small groups at (mostly round) tables. This seating is usually chosen for events that include a seated meal or when the focus is on the interaction between the participants. The individual tables are arranged in relation to one another depending on the type of event.
Cabaret seating is a special form : here the tables are only seated on the sides that allow a view of the stage.
Block seating
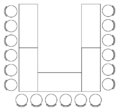
With block seating or table seating , the participants sit at a large (rectangular or oval) table, for example a dining or conference table.
If there are many participants, several long boards can be set up next to each other or in a U, T or E shape. With U-style seating , the head end can only be seated on one side in order to emphasize the participants sitting there. The space requirement is about 3 m² per person. U-shaped seating only makes sense for events with up to 40–60 participants; an E allows up to 90 people.
Other types of seating
The standing reception gets by without chairs ; an aperitif can also be held while standing, but also with seating. Another type of seating without a table is the circle of chairs , the goldfish bowl is a special form .
In the political sphere in particular, there are mixed forms: the delegation leaders sit at the conference table, the other delegation members concentrically behind it.
Meeting room of the UN Security Council .
Choice of seating
The seating is chosen depending on the expected number of participants, the security requirements, the desired feeling of space and comfort, the visibility requirements and the space requirements of the participants. In addition, time requirements when changing between several types of seating and the available space play a role.
The seating of a room can be planned with special software.
Legal requirements
Germany
In Germany, the assembly regulations of the federal states contain requirements for the seating of event rooms. It is about the maximum distance of each place from the closest corridor or exit as well as the width, seat spacing and the "immovable" attachment of the chairs.
literature
- Clemens Porsche: Take a seat. Seating, chairs and furniture . In: Luppold, Stefan / Bühnert, Claus (Hrsg.): Practical manual for congress, meeting and conference management. Concept & design, advertising & PR, organization & financing . Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden 2017, ISBN 978-3-658-08309-0 , p. 705-716 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ seating. In: Duden. Retrieved August 26, 2019 .
- ↑ Clemens Porsche: Take a seat. Seating, chairs and furniture . In: Practical Guide to Congress, Meeting and Conference Management . S. 681 .
- ↑ a b F. Jürgen Herrmann (ed.): The teaching kitchen . 3. Edition. Handwerk und Technik, 2008, ISBN 978-3-582-40045-1 , p. 253 .
- ↑ Hermann Grüner u. a .: The young cook . 36th edition. Pfanneberg, Haan 2015, ISBN 978-3-8057-0701-5 , pp. 218 .
- ^ U-shape: Seating in conference rooms in the form of a U. In: tagungsplaner.de. Retrieved August 28, 2019 .
- ↑ Stefan Lohnert: Space for the spaces of the event . In: Luppold, Stefan / Bühnert, Claus (Hrsg.): Practical manual for congress, meeting and conference management . S. 681 .
- ↑ Jochen Hinken: Professional event management . In: Written management course in 10 lessons . Euroforum, Düsseldorf 2005, p. 53 .
- ↑ a b 7 important types of seating for your events. In: Eventbrite Blog. August 21, 2018, accessed August 26, 2019 .
- ↑ Martin Glöckner: Security requirements for a congress. Public law requirements and liability regulations under civil law . In: Luppold, Stefan / Bühnert, Claus (Hrsg.): Practical manual for congress, meeting and conference management . S. 681 .