Biuret reaction
The biuret reaction , also known as the biuret assay or the biuret test , is a chemical detection reaction for biuret and for proteins , more precisely for their peptide bonds .
Proof principle
Peptide bonds are an integral part of proteins. With the biuret sample, proteins can be detected photometrically in samples.
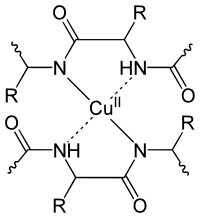
In this protein determination method, compounds with at least two peptide bonds form a colored complex with divalent copper ions in an aqueous-alkaline solution . This results in a color change to dark purple. This detection method is - compared to other staining methods - one of the most unspecific. For example, tyrosine residues also complex copper ions and contribute to the formation of color.
The detection limit is 1 to 10 µg protein per milliliter .
In practice, sodium hydroxide solution is added to the solution to be examined , a little copper sulfate solution is added and shaken. The measurement of the color intensity can take place at 540 to 550 nm .
Despite the name, a biuret is not required for the reaction . Rather, biuret forms a similar complex due to its amide bond and can therefore serve as a positive control .
Further detection reactions for proteins
- Xanthoprotein reaction
- Millon's reaction
- Ninhydrin reaction
- Kaiser test
- Bradford test
- Lowry test
- Folin-Ciocalteu reagent
- BCA test
Individual evidence
- ^ AG Gornall, SJ Bardawill, MM David: Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. In: J Biol Chem. Volume 177 (2), 1949, pp. 751-766. PMID 18110453 .
- ↑ after R. Matissek, G. Steiner: Lebensmittelanalytik. 3., completely revised. Edition. Springer-Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-540-62513-5 , pp. 84f.
- ^ A b F. Lottspeich, JW Engels, A. Simeon (Ed.): Bioanalytik. 2nd Edition. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-8274-1520-9 , p. 38.