Biuret
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Biuret | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 5 N 3 O 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, hygroscopic crystals |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 103.09 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.47 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
188–190 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
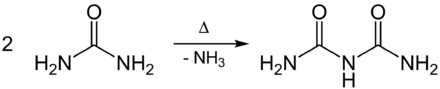
Biuret [ biuˈreːt ] is an organic compound from the group of carboxamides , which is derived from the unstable allophanoic acid ( carbamoylcarbamic acid H 2 N – CO – NH – COOH). Biuret is produced during the pyrolysis of urea by condensation of two molecules of urea with splitting off of one molecule of ammonia .
presentation
Biuret is formed when urea is heated with the elimination of ammonia:
In addition to biuret, small amounts of triuret and melamine are also produced .
Properties and evidence
Biuret is a colorless, crystalline, water-attracting substance, which dissolves little in cold water or ether, but well in hot water ( better in acidic and basic than in neutral due to weak ampholyter properties). Biuret partially turns into melamine when heated. When biuret decomposes above 188 ° C, cyanuric acid and ammonia can also form nitrogen oxides , carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide . Biuret is toxic to plants; even small amounts (50–150 ppm in the nutrient solution) cause chlorosis .
A purple complex forms with copper (II) ions in an alkaline medium . A similar hue can be observed in the so-called biuret reaction with proteins . Here, instead of biuret, the peptide groups act as ligands for the copper ion. This reaction can be used for the detection of proteins in aqueous solutions . In clinical diagnostics, for example, the biuret method according to Weichselbaum can be used to determine the total protein in body cavity effusions ( transudates and exudates ).
use
There is no known industrial use of biuret.
Biuret is present as an impurity in every manufactured urea. When using urea as a fertilizer, the content of biuret is limited (usually less than 1%), as this has an inhibiting effect on healthy plant growth.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on Biuret. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on September 30, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on biuret in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 16, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ European Pharmacopoeia , Deutscher Apotheker Verlag Stuttgart, 6th edition, 2008, p. 543, ISBN 978-3-7692-3962-1 .
- ^ A b Haas, ARC, Brusca, JN: Biuret, Toxic Form of Nitrogen , California Agriculture, 1954 8 ( 6 ): 7, 11.