Blount's disease
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| M92.5 | Juvenile osteochondrosis of the tibia and fibula - Osteochondrosis of the medial condyle of the tibia (Blount's disease) - Tibia vara (Blount-Barber's disease) |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
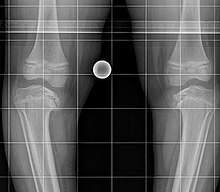
The Blount disease , also Blount's syndrome or Erlacher-Blount's syndrome is the childhood form of the tibia Vara (in humans), a deformation of the shank bone growth as a result of disruption of the medial epiphyseal . The disease was named after the first person to describe it, Walter Putnam Blount (1900-1992). The disease is rare but is more common among the African-born population of South Africa .
Two forms can be distinguished:
- Infantile form in children under 10 years of age, usually in the first few years of life, usually occurring on both sides
- Adolescents, juveniles or late forms mostly between 8 and 15 years of age and appearing unilaterally, often with premature closure of the growth plate and necrosis on the adjacent epiphysis .
Must be distinguished are deformities due to rickets and premature epiphyseal closure of other, mostly post-traumatic genesis.
Classification
According to Langeskjöld, various prognostic and therapy-relevant stages can be distinguished:
- Stage I: Varus deformity with irregularity of the growth plate and medial hook formation
- Stage II: Lowering of the tibial metaphysis medially with a slight incline
- Stage III: Clear varus and pronounced hook medially, possibly fragmentation of the metaphysis medially
- Stage IV: Narrowing of the growth plate with a clear inclination
- Stage V: Additional deformation and division of the epiphysis
- Stage VI: Bridging between the epiphysis and metaphysis, also with partial fusion of the fragmented epiphysis to the medial metaphysis.
treatment
Treatment is usually conservative with splints.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ F. Hefti: Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice . Springer 1998, ISBN 3-540-61480-X .
- ↑ A. Langeskjöld (1952): tibia vara (osteochondrosis deformans tibiae): a survey of seventy-one cases, In: Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica 103, page 1-22
Web links
- Blount Syndrome at whonamedit.com (English)
literature
- A. Greenspan: Orthopedic Radiology. A practical approach. 3rd edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2000, ISBN 0-7817-1589-X
- F. Hefti: Children's orthopedics in practice . Springer 1998, ISBN 3-540-61480-X .