Bootstrapping server function
Bootstrapping Server Function (BSF) refers to a technical intermediary element in mobile radio between previously unknown terminals and servers, which allows mutual authentication and - based on this - the exchange of secret keys. This enables the use of general additional services and applications that require authentication and a secure communication relationship, such as mobile TV .
functionality
architecture
Overall, the following functional elements are involved in maintaining such a generic security relationship (abbreviated). Overall, the structure and mode of operation of these elements are called generic authentication architecture ( GAA) or generic bootstrapping architecture (GBA):
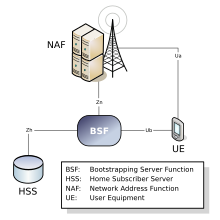
- Terminal, e.g. B. a mobile phone, short User Equipment (UE) that wants to use a certain service
- Application server, e.g. B. for Mobile TV, Network Application Function (NAF) for short; provides the service
- the Bootstrapping Server Function (BSF) itself; mediates a security relationship between UE and NAF
- a home subscriber server (HSS) of the (cellular) network provider; manages the respective user-specific profiles of its terminal users
The term bootstrapping here means the technical function of first establishing a security relationship with a previously unknown device in order to then be able to install security elements (keys) in the device itself and in the BSF.
Essentially, the Diameter and HTTP protocols are used; u. Under certain circumstances, SOAP can also be used between BSF and NAF instead of Diameter .
procedure
The BSF is consulted by the application server (NAF) after a terminal has asked it for service access. Since the application server does not yet know the terminal device at this point in time, it initially refers it to the BSF. The terminal and the BSF are now authenticated on both sides; this is done using the 3GPP AKA (Authentication and Key Agreement) protocol and via requests from the BSF to the Home Subscriber Server (HSS).
The BSF and the terminal (UE) then agree on a session key that is to be used for encrypted data exchange with the application server (NAF). If the end device now turns to the application server again, it can obtain both the session key and user-specific data from the BSF and start the data exchange with the end device (UE). The appropriate session keys are used for cryptographic protection.
The security relationship itself, between the end device and the server, never leaves the sovereignty of the (mobile) network operator; only data (keys) derived from this security relationship can be queried and used by applications.
Norms and standards
BSF is standardized in the newer versions of the 3GPP standards:
- Generic Authentication Architecture (GAA)
- Generic Bootstrapping Architecture (GBA).
For details see below a. 3GPP TS 33.919, 33.220 24.109, 29.109