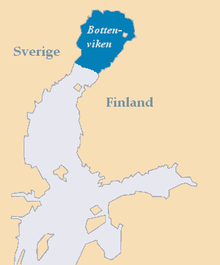
Bottenwiek
The Bottenwiek ( Swedish Bottenviken , Finnish Perämeri ) is part of the Baltic Sea between Sweden and Finland . It forms the northern part of the Gulf of Bothnia and is separated from the Bothnian Sea in the south by the Kvarken strait .
The Bottenwiek lies between 63.5 and 66 degrees north latitude and is therefore the northernmost part of the Baltic Sea. It occupies 10% of the total area and 7% of the volume of the Baltic Sea. The Bottenwiek is on average 40 meters deep. Their salinity is very low at 0.2–0.4%. Several large tributaries such as the Kemijoki , Torne älv , Kalixälven and Lule älv feed the Bottenwiek with fresh water, at the same time the Kvarken , which is only 25 meters deep, forms a threshold that prevents the salt content from being balanced. Due to its northern location, the Bothnia completely freezes over in winter. In the northern areas, the ice cover prevails for 120 days and can reach a thickness of up to one meter. Because of the low salinity and the low temperatures, many plant and animal species that are found in the southern Baltic Sea are missing here. On the other hand, freshwater fish sometimes live in the brackish Bottenwiek .
Coordinates: 65 ° 0 ' N , 23 ° 0' E
Web links
- Website of the Finnish Ministry of the Environment on the Bothnian Bay Life project (Finnish / Swedish / English)