Sekiyado Castle
| Sekiyado Castle | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Sekiyado, replica castle tower |
||
| Creation time : | 1457 | |
| Castle type : | Hirajiro (Lower Castle) | |
| Conservation status: | partially reconstructed elsewhere | |
| Place: | Noda | |
| Geographical location | 36 ° 5 '47.7 " N , 139 ° 46' 48.2" E | |
|
|
||
The castle Sekiyado ( Japanese 関宿城 , Sekiyado-jō ) is located in the city of Noda in Chiba prefecture . In the Edo period , the Kuze last resided there with an income of 50,000 koku as a smaller Fudai daimyo .
Lords of the castle in the Edo period
- From 1616 a branch of Hisamatsu-Matsudaira with 20,000 koku,
- from x a branch of the Nomi-Matsudaira with 26,000 Koku,
- from 1619 a branch of the Ogasawara with 22,000 koku,
- from 1640 Hōjō Ujishige with 20,000 Koku,
- from 1644 a branch of Makino with 17,000 koku,
- from 1656 a branch of Itakura with 50,000 koku,
- from 1669 the Kuze with 50,000 Koku,
- from 1683 again a branch of Makino with 53,000 Koku,
- from 1705 again the Kuze with 50,000 Koku.
history
Sekiyado Castle is said to have been built in 1457 by the Koga ( 古河 氏 ) caretaker, Yanada Shigesuke ( 簗 田 成 助 ;? –1512), on the right bank of the Edogawa River.
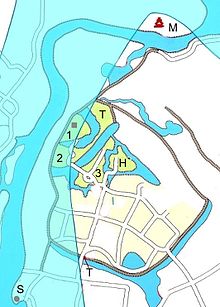
In 1574 the castle was besieged and conquered by the later Hōjō . In 1590 the later Hōjō went under in the fight against Toyotomi Hideyoshi , who left the Kantō plain and thus the castle to Tokugawa Ieyasu . The lords of the castle, beginning with the Hisamatsu-Matsudaira, changed at short intervals before the beginning of the Tokugawa period until the Kuze took over the castle again in 1704 and kept it until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. - The ship traffic on the Edogawa could be controlled from the castle. A memorial stone, [S] in the adjacent plan, marks the location of the checkpoint ( 関 所 , sekijo ).
The attachment
The castle was built within a swamp area on a headland formed by the Edogawa and the greater Tonegawa. It is the northernmost point of the former Shimousa Province . Around an almost square inner castle area [1], separated by a moat, the second castle area [2] was laid out in the south and the third castle area [3] protected by a common moat in the east. In addition there were the preliminary areas Hattan-kuruwa ( 発 端 曲 輪 ; H) and Tenshin-kuruwa ( 天 神曲 輪 ; T).
In the inner castle area, a three-story watchtower ( 三階 櫓 , sangai-yagura ; red square in the inner castle area) was built, which functions as a castle tower ( 天 守 閣 , tenshukaku ). This was renewed by the Kuze in 1671. In 1870 the Han administration building burned down . - The samurai quarter was protected by a wall and in the south by a ditch. In the south was the main gate ( 大 手 門 , ōtemon ; T).
Today most of the inner castle area and the western part of the other areas have disappeared due to the river bed extension of the Edogawa (marked in light blue). Another part became arable land and residential area after 1868. The castle's Uzumi Gate ( 埋 門 ) still exists as a gate to a homestead. A history museum of the prefecture ( ein 県 立 関 宿 城 博物館 , Chiba kenritsu Sekiyado-jō hakubutsukan ) was built north of the former castle area and the three-story castle tower [M] was also rebuilt.
Remarks
- ↑ Hōjō Ujishige ( 北 条 氏 重 ; 1559-1658) was a daimyō from a branch line of the Hōjō, who stood on the side of Tokugawa Ieyasu and was promoted by this. He died with no offspring, so that line became extinct.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Sugai, Yasuo: Sekiyado-jo in: Miura, Masayuki (ed.): Shiro to jinya. Tokoku-hen. Gakken, 2006. ISBN 978-4-05-604378-5 , p. 100.
literature
- Chiba-ken kotogakko kyoiku kenkyukai rekishi bukai (Ed.): Chibta-ken no rekishi sampo. Yamakawa Shuppan, 2001, ISBN 978-4-634-24612-6 , p. 115.