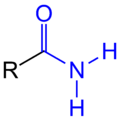
Carbamoyl group
In chemistry, carbamoyl group is a term for the atom grouping –CO – NH 2 in systematic names according to the IUPAC rule C-431.2.
A special structural property of such compounds is the clearly restricted rotatability of the C – N bond. The C – N bond is on average only 132 pm long, which indicates a double bond character resulting from the interaction of the non -bonding electron pair of the nitrogen atom with the carbonyl group .
Due to the delocalization of the non-bonding electron pair from the nitrogen atom into the carbonyl group, carbamoyl-containing compounds are not basic, but rather weak acids with pKa values of around 15.
In peptides , the carbamoyl group is abbreviated as “Cbm–”.
Examples
- Carbamoyl carbamate ( biuret ) contains two carbamoyl groups in one molecule
- 1-carbamoylguanidine
- o -Carbamoylphenoxyacetic acid, an ointment component for the surface treatment of joint and muscle rheumatism, neuralgia and sciatica
Differentiation from the carboxamides
Acetic acid amide is a carboxylic acid amide (often just called “amide” for short) and contains a carbamoyl group. N -methyl acetic acid amide and N , N -dimethyl acetic acid amide also belong to the carboxamides, but neither contain a carbamoyl group.
Individual evidence
- ^ Albert Gossauer: Structure and Reactivity of Biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, 2006, pp. 424-425, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 .
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 1: A-Cl. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1979, ISBN 3-440-04511-0 , p. 539.
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann : Organic Chemistry , 2nd revised edition, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, p. 468, ISBN 3-342-00280-8 .
- ^ Siegfried Ebel and Hermann J. Roth (editors): Lexikon der Pharmazie , Georg Thieme Verlag, 1987, p. 579, ISBN 3-13-672201-9 .