Carbonyl dyes
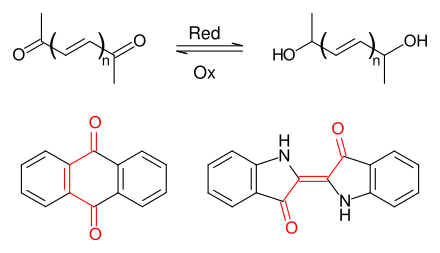
Carbonyl dyes are dyes which have at least two conjugated carbonyl groups as a common structural element . Both the anthraquinone dyes and the indigoid dyes belong to the group of carbonyl dyes . The most important natural dyes - indigo , purple , alizarin and carmine - have this partial structure. The most important synthetic carbonyl dyes are based on anthraquinone .
The main advantages of carbonyl dyes are, on the one hand, the possibility, which is advantageous in industrial applications, of reducing the carbonyl groups to water-soluble dienols (→ vat dyes ). On the other hand, by introducing suitable electron donor substituents, the absorption maximum of the resulting dyes can be shifted into almost every region of the VIS spectrum .
Reduction / oxidation of carbonyl dyes / examples: anthraquinone and indigo
Individual evidence
- ^ Heinrich Zollinger: Color Chemistry: Syntheses, Properties, and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments . 3. Edition. WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2003, ISBN 3-906390-23-3 , p. 255 ff . ( limited preview in Google Book search).