Anthraquinone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
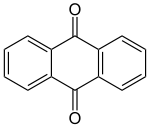
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Anthraquinone | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 8 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
rhombic, pale yellowish-green, odorless needles |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 208.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.44 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
286 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
380 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
13 m Pa (50 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data |
|
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Anthraquinone is a quinone derived from anthracene . It was first made in 1836 by Auguste Laurent by oxidizing anthracene.
Occurrence
Anthraquinone occurs naturally in the form of the rare mineral hoelite . Anthraquinone derivatives are the active ingredients of various herbal laxatives : rhubarb root , buckthorn bark , cape aloe , senna leaves and buckthorn berries .
Extraction and presentation
Anthraquinone can be explained by the oxidation of anthracene with nitric acid or chromic acid produced.
However favorable the reaction of benzene and phthalic anhydride by Friedel-Crafts . This initially creates an oxocarboxylic acid, which can then be converted into anthraquinone with sulfuric acid .
properties
Unlike most quinones, anthraquinone is not steam volatile. Opposite oxidants by anthraquinone is quite insensitive, reducing agents , however, easily anthraquinone or anthrone convertible. This ability to reduce forms the basis for linking anthraquinones to dianthrones and polyanthrones . The introduction of functional groups into the molecule (e.g. hydroxyl and amino functions ), especially in positions 1, 4, 5 or 8, increases the intensity of the color and changes the color. It can be varied from yellow to purple. The flash point is 213 ° C.
use
Anthraquinone is an important raw material for the production of anthraquinone dyes , for example alizarin . 2-Alkylanthraquinones (e.g. 2-ethylanthraquinone ) serve as a catalyst in the industrial production of hydrogen peroxide by the anthraquinone process .
Furthermore, it was used under the name Morkit as a means to ward off bird damage after sowing for dressing the seeds (e.g. maize). On January 20, 2009, on the recommendation of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), the EU Commission withdrew anthraquinone approval as a repellent due to health concerns for users and consumers.
safety instructions
Due to health concerns for users and consumers, anthraquinone was withdrawn from approval as a plant protection product in the EU in 2009. Anthraquinone has been classified by the International Cancer Research Agency of the WHO (IARC) as possibly carcinogenic for humans (category 2B). The announcement was made in 2011 in the journal Lancet Oncology , the rationale was published in the 2013 monograph. In February 2013, the Federal Institute for Risk Assessment withdrew its recommendation for the use of anthraquinone in food packaging and announced a reassessment of the substance under chemical law.
At the suggestion of the German chemicals authority, the chemical classification of anthraquinone was revised in 2015. The Committee for Risk Assessment (RAC) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) changed the classification for anthraquinone on December 4th, 2015 as follows: Anthraquinone is classified as carcinogenic Carc 1B, the warning was set to H350. This classification of the RAC has yet to be implemented by the EU Commission in applicable law, but with the publication it represents the state of knowledge that must be taken into account by companies and authorities. On June 27, 2017, an action against the classification was filed with the European Court of Justice .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on anthraquinone. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 12, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on anthraquinone in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 29, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Anthraquinone in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on December 29, 2019. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Hoelite at mindat.org (English).
- ^ Association of authors: Organikum , 19th edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig · Berlin · Heidelberg 1993, ISBN 3-335-00343-8 , p. 383.
- ^ Association of authors: Organikum , 19th edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig · Berlin · Heidelberg 1993, ISBN 3-335-00343-8 , p. 340.
- ↑ To ward off birds in agriculture .
- ↑ a b Reasoned opinion on the review of the existing maximum residue levels (MRLs) for anthraquinone according to Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 . In: EFSA Journal . tape 10 , no. 6 , 2012, p. 2761 , doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2012.2761 .
- ↑ IARC Monograph 101 , Chapter Anthraquinone.
- ↑ Federal Institute for Risk Assessment: BfR removes anthraquinone from the BfR recommendations for food packaging. BfR Opinion No. 005/2013 of February 12, 2013.
- ↑ RAC decision of December 4, 2015 .
- ↑ Official Journal of the EU of September 4, 2017 (PDF) .
See also
- Anthraquinones as an active ingredient group in herbal medicine
Web links
- FAZ.NET : Nanotechnology: An organic molecule as a burden bearer ( Memento from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ), January 23, 2007
- From color to active ingredient - easier synthetic access to interesting anthraquinones


