Steam dome
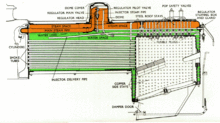
The steam dome ( loan translation from English steam dome , actually " steam dome ") is part of the steam locomotive boiler . It is riveted or welded onto the top of the long bowl and is visible to the outside as a round bowl structure. If the lower end of the steam dome is flared up by flanging, it is also known as the "dome part".
In the long boiler, the steam required for the engine and the auxiliary units, such as the feed pump, steam jet pump , auxiliary blower , air pump , steam pipe and the heating devices, is generated. The boiler is filled to approx. 75% to 80% with water. In the remaining part, in the so-called steam space, the resulting steam is collected. Since steam as dry as possible is required for operation, the distance between the water surface and the steam extraction point is increased by adding a steam dome. Water particles that are entrained into the steam space by vigorous evaporation can hardly get into this high-lying part of the boiler. In addition, deflector plates are installed in the steam dome. The steam flows around them, any residual water drips off.
The amount of steam required for operation is regulated from the driver's cab via a regulator , which is located in the steam dome depending on the type of locomotive. Due to this type of installation, the steam extraction pipes for the auxiliary units of the boiler and the locomotive also extend from the steam dome.
For large steam locomotives, e.g. B. at the Deutsche Bundesbahn , several steam domes were put on. A regulator dome and a dome for wet steam extraction were provided for the auxiliary units.
literature
- M. Weissbrod, R. Barkhoff: The steam locomotive - technology and function Part 1: The boiler and the history of the steam locomotive . Merker Verlag GmbH, Fürstenfeldbruck 1994, ISBN 3-922404-03-0 .
- Röll: Encyclopedia of Railways , Vol. 3, 1912, p. 225.