Big water flea
| Big water flea | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
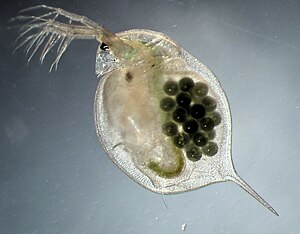
Great water flea ( Daphnia magna ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Daphnia magna | ||||||||||||
| Straus , 1820 |
The great water flea ( Daphnia magna ) is a species of the genus Daphnia ( Daphnia ).
The females grow up to 6 millimeters, the males about 2 millimeters. Rows of thorns mark the back strip on the bowl. The head keels on the side are continued over half the length of the hull shell in the form of spiked strips. The tail spine is of different lengths. The shells have a clear field. Directly in front of the anus , the dorsal edge of the abdomen has a noticeable indentation. The first antennae protrude far from under the short rostrum . The second antennae have feathered row bristles. The intestine has 2 "liver squirrels". The large water flea is a heat-loving form of pond that occurs in abundance in waters with a high nutrient content.
Daphnia magna is commonly used for daphnia testing . A publication published at the end of 2019 suggested the harmfulness of microplastics for organisms.
supporting documents
- Heinz Streble , Dieter Krauter : Life in a drop of water. Microflora and microfauna of freshwater. An identification book. Franckh-Kosmos Verlag, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-440-11966-2 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Christoph Schür, Sebastian Zipp, Tobias Thalau, Martin Wagner: Microplastics but not natural particles induce multigenerational effects in Daphnia magna . In: Environmental Pollution . December 2019, p. 113904 , doi : 10.1016 / j.envpol.2019.113904 .