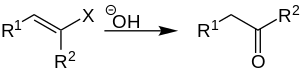
Eltekoff hydrolysis
The Eltekoff hydrolysis is a name reaction in organic chemistry , which was first introduced in 1873 by A. Eltekoff and named after him. It is the hydrolysis of vinyl halides in an aqueous alkaline solution to produce carbonyl compounds ( aldehydes or ketones ).
Overview reaction
In this reaction, a vinyl halide is converted into a ketone (or aldehyde) using a base .
Reaction mechanism
First there is a nucleophilic attack 1 by the hydroxide ion on the carbon of the olefin, which is in the β position to the halogen . The now negatively charged carbon in the α position then attacks a hydrogen atom of the water molecule nucleophilically 2 . The deprotonation of the water creates a hydroxide ion , which then attacks the carbon in the α-position of the halogen alcohol formed in a nucleophilic manner 3 . This enables the halogen to be split off as an anion . When heated, the electron pairs in the resulting glycol rearrange 4 and one of the two hydroxide groups goes off together with a proton as water. Due to the keto-enol tautomerism , the end products are both an enol 5 and a ketone 6 .
application
This reaction is used to make glycols, aldehydes and ketones.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Zerong Wang: Eltekoff Hydrolysis . In: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents . Wiley, 2010, ISBN 978-0-470-63885-9 , pp. 986-988 , doi : 10.1002 / 9780470638859.conrr214 .