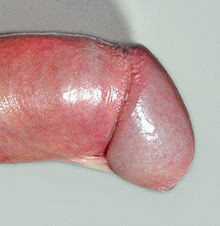
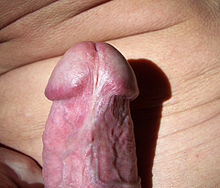
Frenulum breve
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| N48.8 | Frenulum breve |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The frenulum breve (from Latin frenulum 'ribbon' and brevis 'short') is a mostly congenital shortening of the foreskin ligament ( frenulum praeputii ) between the inside of the penis foreskin and the underside of the penis shaft.
root cause
The frenulum breve is usually congenital, but can also be caused by (repeated) inflammations such as balanoposthitis (glans foreskin inflammation) or by skin diseases of the foreskin (such as lichen sclerosus ).
Clinical manifestations
The foreskin ligament should normally be long enough to allow the foreskin to retract completely so that it rests smoothly on the penile shaft. The foreskin ligament is too short if it is difficult or impossible to retract the foreskin. Under certain circumstances, which is acorn (glans penis) upon retraction of the foreskin or the erection bent of the penis due to the resulting train, which can be painful. The shortened foreskin ligament can tear under mechanical stress. If the artery in the foreskin ligament ( arteria frenularis ) is injured, heavy bleeding can occur. If the torn foreskin ligament heals, the scarring can shorten it further. A frenulum breve can lead to dyspareunia . Some authors associate the presence of a frenulum breve with premature ejaculation ( eiaculatio praecox ), the relative frequency given by them was assessed as too high.
diagnosis
The diagnosis is made by inspection .
treatment
A frenulum breve can be treated surgically with a frenulotomy (syn. Frenuloplasty). During this operation, the frenulum is incised horizontally and the resulting mucosal defect is sutured vertically. If there is an accompanying phimosis (narrowing of the foreskin), a circumcision (male circumcision) with frenuloplasty can be performed. If the bleeding is excessive due to injury to the artery, it must be pierced . The operations are usually carried out on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia .
The use of cortisone- containing ointments can be considered for non-surgical treatment . In the case of superficial tears in a frenulum breve, healing without functionally limiting scars is possible. It should temporarily to sexual intercourse or masturbation is no need not to burden mechanically around the crack location.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Rolf Eichenauer, Joerg Sandmann, Harald Vanherpe: Clinic Guide Urology. 3rd edition, Urban & Fischer, 2003, ISBN 978-3-437-22790-5 , p. 449.
- ^ A b Peter Whelan: Male dyspareunia due to short frenulum: an indication for adult circumcision. In: BMJ. Volume 2, number 6103, 1977, pp. 1633–1634, doi : 10.1136 / bmj.2.6103.1633-a , PMC 1633287 (free full text)
- ↑ a b c d Dirk Manski: Frenulum breve: short foreskin ligament . In: urologielehrbuch.de . Retrieved May 22, 2020.
- ↑ a b c Bernhard Stier, Nikolaus Wiessenrieder, Karl Otfried Schwab (ed.): Adolescent medicine. 2nd edition, Springer, 2018, ISBN 978-3-662-52782-5 , p. 320.
- ↑ Luigi Gallo, Sisto Perdona, Antonio Gallo: The Role of Short frenulum and the Effects of Frenulectomy on Premature Ejaculation. In: The Journal of Sexual Medicine. Volume 7, number 3, 2010, pp. 1269-1276, doi : 10.1111 / j.1743-6109.2009.01661.x .
- ↑ Emmanuele A Jannini: Words of Wisdom. Re: The Role of Short Frenulum and the Effects of Frenulectomy on Premature Ejaculation. In: European Urology. Volume 57, number 6, 2010, pp. 1119–1120, doi : 10.1016 / j.eururo.2010.03.027 .
- ^ Judith Dockray, Alexander Finlayson, Gordon H. Muir: Penile frenuloplasty: a simple and effective treatment for frenular pain or scarring. In: BJU International. Volume 109, number 10, 2012, pp. 1546-1550, doi : 10.1111 / j.1464-410X.2011.10678.x .