Raised bed
The raised bed is a variant of the classic (ground-level) bed system or, depending on the filling in the layer structure, a variant of the hill bed . Raised beds are garden beds that are not laid out at ground level, but rise above the usual bed level. It is particularly common in near-natural horticulture .
The raised bed combines the following essential features: Eliminating the need to stoop when gardening by raising the bed; very few weeds as the main flight of seeds takes place on the ground; no snails if a snail fence is put in place; the use of the heat of rotting from below (at the roots) through the layered structure and, associated with this, significantly faster growth. By also attaching a cover, the raised bed can also be used as a cold frame . Due to the emerging trend of urban horticulture , raised beds are also enjoying increasing popularity in urban areas. The reason for this is that no green space is required to run a garden and, accordingly, it is also possible to plant on terraces, backyards or entrance areas.
construction
The following reasons for creating such a variant of the garden bed can be mentioned:
- an earlier warming of the bed,
- unsuitable, i.e. not deep or nutrient-poor garden soil,
- optimal recycling of garden waste,
- Barrier-free operation of a garden.
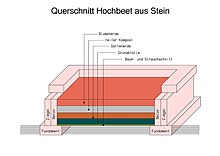
The raised bed also offers the gardener the opportunity to use rotting materials, such as garden waste, in the garden himself. A close-meshed wire mesh - such as an old wire fence - against voles and other rodents can be built in on the ground as a basis. Then follows tree pruning, shrub pruning approx. 30 cm garden waste, leaves and lawn cuttings, ripe compost, ripe manure approx. 20 cm, garden soil approx. 25 cm.
Refilling a raised bed can be carried out as follows: Put the top layer (garden soil) on one side. Then you fill up the middle layer (leaves and lawn clippings, ripe compost, ripe manure); this layer should again provide rotting heat and nutrients; then you distribute the garden soil evenly again. This has the following advantages:
- again the full filling height,
- the nutrients and the fresh soil created by the rotting are well mixed in the planting layer,
- a new layer of rotting beneath the roots and thus again rotting heat,
- no need for new garden soil.
Furthermore, a raised bed is not dug up , which ensures that the stratification of the soil and the fauna that has formed are not mixed up. This is not the case with traditional horticulture.
Special forms
The table bed is a special form of raised bed.
With this special form, for example, wheelchair users do not have to forego using the garden. The bedding plants can be cared for safely and comfortably while sitting. A tub-like recess with a basin height of 20 to 30 cm contains a plant substrate, the composition and thickness of which depends on the location requirements and the desired planting. Circular table beds are particularly easy to walk around with a wheelchair.
Another special form, which is mainly used in development work, but also among hobby gardeners, is the so-called keyhole garden .
The potato barrel is similar to a raised bed . This is used by the hobby gardener to plant potatoes in household quantities with little space requirement.
investment
A raised bed is box-shaped, rectangular and, if possible, in a north-south direction (solar radiation). It is important to cover the base of the raised bed with a fine-meshed wire mesh . This can prevent rodents like mice from entering . You can fill the bed either with just soil or, if you want, with different layers (soil, wood, compost ). When creating the bed, you should also pay attention to the length and width, otherwise the processing ( removing weeds , watering, weeding) is accompanied by an uncomfortable posture.
In order to achieve the best effect and a good yield, the raised bed should be completely emptied every five to seven years and then filled again as with a new plant.
It can be bordered with a wide variety of materials as you wish:
- natural wood (ideally larch wood due to its resilience),
- Natural stone ,
- Artificial stone ( concrete slabs , brick etc.),
- Sheet metal , corrugated iron ,
- Stone ,
- Plastic ,
- Stable wire mesh baskets such as gabions (with additional sealing of the mesh, for example with organic materials such as jute fabric or coconut mats).
The sides of the raised bed should be made so stable that they can withstand the not inconsiderable earth pressure of the introduced soil layers. The inside of the edging of raised beds should be protected with a moisture barrier or paint when using moisture-prone materials.
photos
Raised bed made of natural stone
See also
- Vegetable patch
- seedbed
- Deep cultivation bed
- Perennial bed
- Carpet bed
- Cottage garden
- Herb spiral
- Gardener construction
Web links
literature
- Brigitte Kleinod: The raised bed - a wide range of design ideas for vegetable, herb and flower gardens . pala, 2009, ISBN 978-3-89566-261-4 .
- Sofie Meys: The raised bed for vegetables, herbs and flowers . Leopold Stocker, 2012, ISBN 978-3-7020-1351-6 .
- Gernot Kosok-Pokorny, Siegfried Stein: Raised beds - Build and plant yourself . blv, 2013, ISBN 978-3-8354-1083-1 .
- Hudak, Renate; Harazim, Harald: Raised beds, clever gardening and a rich harvest . Gräfe and Unzer, 2015, ISBN 978-3-8338-4729-5 .
- Storz, Sascha: Original raised beds . Bassermann, Munich, 2015, ISBN 978-3-8094-3314-9 .
- Nüsslein-Müller, Susanne: Raised bed gardening . BLV Buchverlag GmbH & Co. KG, 2016, ISBN 978-3-8354-6196-3 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Term: raised bed. Retrieved June 18, 2016 .
- ↑ Joachim Mayer & Judith Starck: The large GU Praxishandbuch garden . 5th edition. Gräfe and Unzer, Münster 2010, ISBN 978-3-7742-6978-1 , p. 377-379 .
- ^ Bavarian State Ministry for Food, Agriculture and Forests. Retrieved December 8, 2019 .
- ↑ Raised beds function. Retrieved June 18, 2016 .
- ^ Landesbetrieb Landwirtschaft Hessen: Tischbeet. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on July 5, 2016 ; Retrieved July 5, 2016 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Kirchplatzgärtchen Ginnheim on anstiftung.de (accessed on April 28, 2018)