Testicular hypoplasia
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| Q55.1 | Hypoplasia of the testicle and scrotum |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
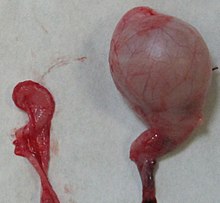
The testicular hypoplasia (Kleinhodigkeit) is a genital malformations with the formation of too small testes . It is often innate and / or a consequence of cryptorchidism , but it can also be acquired. The tissue consistency and the sperm count are usually reduced. A complete absence of one or both testicles is referred to as testicular aplasia or anorchia or monorchism , the shrinkage of an originally normally developed testicle as testicular atrophy .
In humans, testicular hypoplasia occurs in some syndromes ( Goeminne syndrome , Klinefelter syndrome , Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome ) or as a result of androgen deficiency . Testicular hypoplasia is relatively common in pets. In infertile boars, almost a quarter of the affected animals show testicular hypoplasia. In horses, testicular atrophy is observed in up to 3% of stallions; in young racehorses too hard training before they are physically mature is also discussed as the cause.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Wolfgang Baumgärtner, Achim Dieter: Special pathology for veterinary medicine. Thieme, Stuttgart 2015, ISBN 978-3-8304-1174-1 .
- ^ Katrin Rehme: Clinic at the end of the line: the contents of this work are mainly based on the compendium "AllEx - Everything for the exam"; Script. 15, anamnesis, key symptoms. Thieme, Stuttgart 2014, ISBN 978-3-13-174491-3 , p. 143.
- ↑ Walter Busch, Alois Holzmann: Veterinary andrology: Physiology and pathology of reproduction in male animals . Schattauer Verlag, 2001, ISBN 9783794519552 , p. 323.
- ↑ Christine Aurich: Reproductive medicine in horses: Gynecology - Andrology - Obstetrics. Thieme, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-8304-4196-0 , p. 275.