Arches foot
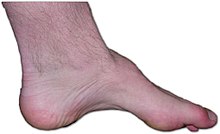
The hollow foot (lat. Pes cavus or Pes excavatus ) is a congenital or acquired deformity of the foot .
Symptoms and ailments
Pressure sores at the highest point of the instep , the sole of the foot, the ball of the foot, and the toes , which can cause foot pain and difficulty walking . The toes are very curved and stiff. The shoes wear out easily on the ball of the foot and on the outer edge. Sprains are more common.
causes
A high arch is usually congenital, familial. Other causes are paralysis , Friedreich's ataxia and nerve damage to the foot muscles . A weakness of the foot muscles and ligaments can also be the cause. Sometimes the arches foot is the first sign of muscle weakness or muscle disease .
Consequences and complications
The unsteady gait and the slight twisting of the foot promote falls and sprains .
treatment
Insoles can support the arch of the foot and relieve the forefoot. Shoes with a high shaft give the foot support and prevent it from twisting. Usually orthopedic shoes are necessary. In severe cases, surgery is possible.
