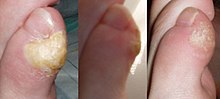
Callus
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| L84 | Corns and horns (skin) calluses |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
A callous or skin callus (technically Tylom , Tylosis or Tylositas ), colloquially also called "cornea", is scarring of the skin with local thickening of the stratum corneum ( hyperkeratosis ). It occurs as a result of a chronic - traumatic dermatitis on. The most famous form of the horn calluses is the so-called corn on the foot .
Emergence
Under mechanical stress, through pressure or friction, minimal inflammation occurs in the skin . To protect the underlying, sensitive cell layers, the skin - limited locally to the stressed region - is stimulated to increase the formation of keratinocytes or corneocytes , which results in a thickening of the stratum corneum ( proliferation hyperkeratosis ).
The formation of callouses typically occurs primarily on the soles of the feet and palms as a result of the special, sometimes job-related stresses caused by pressure and friction. However, this is also possible in other parts of the body if the load is appropriate.
treatment
It is not uncommon for the horny callus to disappear on its own when the triggering mechanical stimulus ends. Pumice stones , Hornhautraspeln and -hobel offered, rasping or cutting off the unwanted cornea. Treatment with horn-loosening substances ( keratolytics ) is also possible. Salicylic acid is usually used. In some cases, surgical correction must be made.
However, horn calluses can also be desirable because they represent a natural protective mechanism of the body and protect the skin from mechanical stress (e.g. when walking barefoot , when working with the hands or when playing musical instruments such as guitars ).