Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting
Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting [ ˈɪntɪɡɹeɪtɪd ˈsɜːvɪsɪz ˈdɪdʒɪtəl ˈbɹɔːdkɑːst ] (ISDB) is a standard for digital media transmission based on MPEG-2 (in Japan), H.264 , or HEVC (for ISDB-S3). It was introduced in Tokyo in 1999 and provides for the distribution of HDTV , SDTV , audio and text in three variants ISDB-T, ISDB-S and ISDB-C.
ISDB-T allows several modulation methods that do justice to the diverse content. The information can be stored in a bit pattern in such a way that mobile end devices receive data in reduced quality with a lower bandwidth ( mobile television ). Other devices receive additional information that improves the quality of the images.
ISDB-T
Terrestrial version.
1seg
Part of the ISDB-T signal for devices such as telephones.
In Japan 1seg broadcasts at 15 frames per second, in Brazil it is 30. You have to pay attention to the capabilities of the device you buy.
ISDB-Tmm
Derived from 1seg for more modern mobile devices.
ISDB-Tsb
Derived from 1seg which only carries audio.
ISDB p
Brazil has made improvements (for example, H.264 ) that have been translated by the SBTVD, ISDB-Tb, ISDB-T International or SATVD (Argentina) standard. This standard is offered worldwide by Japan and Brazil.
MPEG-H Audio , HLG and SL-HDR1 were added to ISDB-Tb in 2019.
ISDB-C
Wired version.
ISDB-S
Satellite version.
ISDB-S3
New satellite version that supports 4K, 8K, HDR, HFR and 22.2 audio.
future
A new terrestrial version should be proposed in 2020 and approved in 2021.
This should be able to support 4K, 8K, HDR, HFR and immersive audio.
It has been suggested to use VVC video compression .
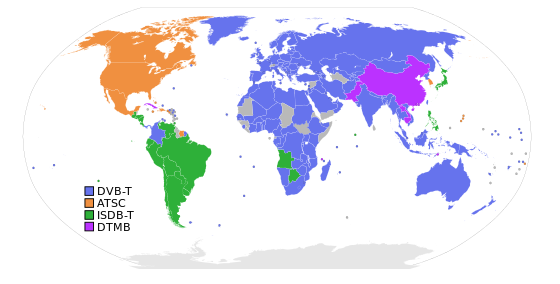
Distribution of the terrestrial ISDB-T variant
In Japan, audio, video and data services are broadcast under the name 1seg via radio transmissions in the ISDB-T standard. ISDB-T is used under the name SBTVD (also called ISDB-Tb) as wireless digital television transmission in Brazil. Argentina and Peru are said to have already adopted the ISDB-T standard. In countries like Bolivia, Chile, Ecuador and Venezuela, the standard for digital terrestrial television and radio is still being tested.
The following table shows the list of countries that have officially introduced the SBTVD and ISDB-T systems.
| America | Asia | Africa |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
Web links
- Specification ( Memento from October 23, 2002 in the Internet Archive )
Individual evidence
- ^ ISDB-C, Cable Television Transmission for Digital Broadcasting in Japan . NHK (Japan Broadcasting Corporation). Retrieved January 15, 2015.
- ↑ https://www.arib.or.jp/english/std_tr/broadcasting/std-b63.html
- ^ Forum Brasileiro de TV Digital Terrestre: Documentation. 2016, accessed May 2, 2020 .
- ↑ Argentina has decided against the European DVB-T standard (Digital Video Broadcasting-Terrestrial).
- ↑ Digital TV: Argentina adopts Japanese TV standard. August 31, 2009, accessed May 2, 2020 .
- ↑ dtv.net: dtv-status net. 2016, accessed May 2, 2020 .