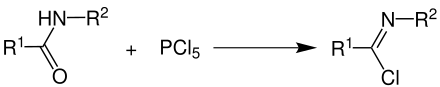Imide chlorides
Imide chlorides (also imidic acid chlorides , imidoyl chlorides or carboxylic acid chloridides ) are a group of chemical compounds which have the functional group R 1 ClC = NR 2 , where R 1 and R 2 can be any organic radicals or hydrogen. They are derivatives of carboxylic acids , are similar to carboxylic acid chlorides and have been known for over 100 years.
Manufacturing
The synthesis of imide chlorides can be done by adding phosphorus pentachloride to carboxamides :
use
Imide chlorides occur in many organic syntheses - such as the nitrile synthesis, Vilsmeier-Haack reaction or the Von-Braun-Rudolph synthesis - as starting materials or intermediates.
Nitrile synthesis
If the amides, which are used as starting materials for the production of imide chlorides, are unsubstituted on the nitrogen, nitriles 1 are easily formed after the formation of the imide chloride with the release of hydrogen chloride :
Manufacture of the Vilsmeier reagent
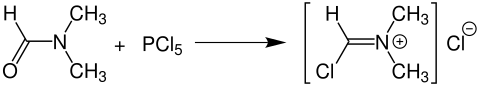
If the reaction to produce an imide chloride is carried out starting from N , N -dimethylformamide , the Vilsmeyer reagent is produced, which is required, for example, for the important Vilsmeier-Haack reaction and thus, among other things, for the production of vanillin :
Reactions
Imide chlorides react with many reagents. Some of these are listed below.
Reaction with water
Imide chlorides reform the corresponding amide after adding water:
Reaction with hydrogen sulphide
With the addition of hydrogen sulfide, imide chlorides form the thionamide corresponding to the amide :
Reaction with primary amines
If one equivalent of an imide chloride is reacted with two equivalents of a primary amine, amidines are formed:
Reaction with hydrogen chloride
When hydrogen chloride is added, imide chlorides react to form iminium chloride cations: