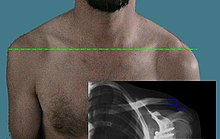
Shoulder joint dislocation
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| S43 | Dislocation , sprain and strain of the joints and ligaments of the shoulder girdle |
| S43.1 | Dislocation of the sternoclavicular joint |
| S43.5 | Sprain and strain of the acromioclavicular joint |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The shoulder joint dislocation (also shoulder joint explosion , AC joint explosion , ACG explosion or AC explosion ) is a complete or incomplete explosion of the shoulder joint caused by traumatic external influences (e.g. fall on the shoulder ) (the meeting of the collarbone and shoulder bone forms the tip or the roof of the shoulder; ACG = acromioclavicular joint).
etiology
Unphysiological stress on the shoulder joint by falling on the outstretched arm, falling on the shoulder or direct force acting on the joint results in a dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint . Depending on the extent of the injury, the acromioclavicular ligaments (lig. Acromioclavicular ligament) and the coracoclavicular ligament (lig. Trapezoidal ligament, lig. Conoidal ligament) can be overstretched as a result. Vertical and horizontal instability can occur depending on the severity.
clinic
In addition to injuries to the skin ( abrasions , hematoma ), a protrusion in the area of the joint and a higher position of the clavicle even when the acromioclavicular ligament ruptures. In the case of a complete rupture (Tossy 3) and also indicated in the case of larger partial ruptures, the usually painful "piano key phenomenon" can be triggered during the physical examination: the outer end of the collarbone, which deviates upwards, can be pushed down by the examiner like a piano key, but it springs when Immediately release the pressure upwards. The extent of the piano key phenomenon is an indirect indication of the extent of the ligament injury.
Classification
According to Jerome D. Tossy , the ACG lesion is divided into three grades depending on the extent of the injury:
- Tossy I = small tears in the ligament structures (only conservative treatment necessary)
- Tossy II = larger tears to partial ruptures of the ligament structures (surgical treatment optional, but rare)
- Tossy III = complete rupture of the entire shoulder-stabilizing ligament structure (surgical treatment can be recommended for younger patients, but conservative treatment is also possible).
The Rockwood classification is newer and more precise
- Rockwood I : pulled to partial tear of the capsule / ligament apparatus. No shoulder joint instability. There is slight tenderness on pressure and slight pain when moving. There is no clear dislocation in the X-ray (corresponds to Tossy I).
- Rockwood II : partial tearing of the capsule / ligament apparatus (rupture of the acromioclavicular ligaments) with partial dislocation of the shoulder joint and a strain of the coracoclavicular ligaments. There is pain on movement and a slight subluxation of the peripheral part of the clavicle. The x-ray shows an enlarged joint space and the lateral clavicle has stepped up by 1/2 the width of the shaft (corresponds to Tossy II).
- Rockwood III : rupture of the entire capsule / ligament apparatus (rupture of the acromioclavicular ligaments and the coracoclavicular ligaments) with complete dislocation of the shoulder joint in the vertical plane towards the head, so-called shoulder joint dislocation. In the clinical examination there is a step formation. The X-ray shows a step higher by a shaft width (corresponds to Tossy III).
- Rockwood IV : The lateral end of the collarbone is dislocated in the horizontal plane through partial detachment of the deltoid trapezoid fascia . There is a rupture of the deltoid insertion and an associated dislocation dorsally through and possibly into the trapezius muscle . A ventral dislocation due to avulsion of the trapezius muscle is very rare and not included in the classification. The X-ray shows a dorsal translation in the axial image.
- Rockwood V : Extreme elevated collarbone with extensive detachment of the muscle attachments at the lateral end of the collarbone with horizontal and vertical instability.
- Rockwood VI : Dislocation of the lateral end of the collarbone to the foot under the coracoid or under the acromion . Rib fractures , clavicle fractures and lesions of the brachial plexus can be found as frequent accompanying injuries .
Diagnosis
An X-ray is performed in three planes for standard diagnostics. The axial recording is used to determine a horizontal translation (Rockwood 4). In cases of doubt, recordings of both shoulders are made for comparison. This can be done as a panoramic shot of the entire shoulder girdle . The examination with weights (5 to 10 kg) on the wrists is more sensitive than images without. Due to the radiation exposure, this examination is increasingly playing a subordinate role.
therapy
In principle, no surgical therapy is indicated for Tossy I and II, but conservative care with a Gilchrist bandage or Desault bandage for one week together with physiotherapy and analgesia . Rockwood IV-VI shoulder joint dislocations are mainly treated surgically. In the event of accompanying injuries or if conventional therapy is not indicated, several surgical systems are available depending on the severity of the injury:
- Kirschner wire
- Wire loop (cerclage)
- Hook plate
- Bosworth screw
- TightRope system (minimally invasive surgical technique)
literature
- Adam Greenspan: Skeletal Radiology. Elsevier, Urban & Fischer, 2007, ISBN 978-3-437-23061-5 .
- Joachim Grifka, Jürgen Krämer: Orthopedics, trauma surgery. Springer, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-28874-6 .
- Fritz Uwe Niethard, Joachim Pfeil, Peter Biberthaler: Orthopedics and trauma surgery. (= Dual row). Thieme, 2014, ISBN 978-3-13-130817-7 .