Node surface
A nodal surface describes the apparently fixed minimum interference of a multi-dimensional standing wave :
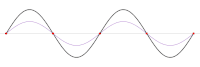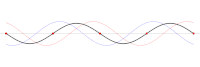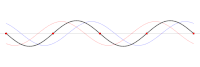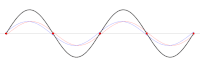
- One-dimensional standing waves (e.g. guitar strings ) swing around (zero-dimensional) point-shaped wave or vibration nodes
- Two-dimensional standing waves (e.g. gong ) swing around (one-dimensional) line-like node surfaces
- Three-dimensional standing waves swing around (two-dimensional) node surfaces.
Important applications can be found in electrical engineering , in vibrating musical instruments and in theoretical chemistry :
One-dimensional standing wave (as the superposition of two opposing traveling waves , red and blue). Zero-dimensional nodes marked in red
Two-dimensional standing wave.
The (unmoved) one-dimensional, line-like node surface has the shape of an X through the fixed point in the middleTwo-dimensional standing waves in music:
Chladni modes of a guitar top with linear nodesThree-dimensional standing waves in chemistry:
probability densities of the first (1s) and second (2s, 2p) electron shell .
The nodal surfaces of the 2p orbitals can be seen as constrictions.Two-dimensional node surfaces on the standing wave of the exhaust gas jet of an afterburner