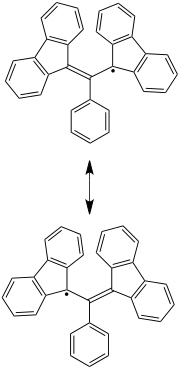
Koelsch radical
In chemistry, the Koelsch radical , even Kölsch radical, a particularly stable carbon -centered radical . This is due to the large number of exceptionally stable mesomeric boundary structures.
Manufacturing
The reaction of α, γ-bisdiphenylene-β-phenylallyl chloride with mercury leads to the formation of the Koelsch radical.
Reactivity
It can be converted into various other chemical substances, a "blue anion, a dianion radical of presumably yellow color and a red trianion".
designation
The Koelsch radical was named after C. Frederick Koelsch , professor of organic chemistry at the University of Minnesota .
Individual evidence
- ^ Ulrich Lüning: Organic reactions , 2nd edition, Elsevier GmbH, Munich, 2007, pp. 19-23, ISBN 978-3-8274-1834-0 .
- ^ CF Koelsch: Syntheses with Triarylvinylmagnesium Bromides. α, γ-Bisdiphenylen-β-phenylallyl, a Stable Free Radical , Journal of the American Chemical Society 79 (1957) 4439-4441 ( doi : 10.1021 / ja01573a053 ).
- ↑ Josef Houben , Theodor Weyl : Methods of Organic Chemistry : Organometallic Compounds Li, No, K, Rb, Cs, Cu, Ag, Au, Volume 11; Volume 13, Georg-Thieme-Verlag, 1970, p. 442 ( online ).
- ↑ Prof. Emeritus C. Frederick Koelsch chem.umn.edu.