Cornet (organ)
The cornet (French, English: Cornet , Spanish: Corneta , term for zinc ) is an organ register . It is a non-repeating, third-containing mixed manual part. In the pedal work , the reed register trumpet 2 'or 1' is often referred to as a cornet .
Executions
The cornet is often only available for the treble range of the manual. The scale ranges from very wide (France) to principled (Spain). In French organs it is used to strengthen the reed register in the high registers. Otherwise the cornet is also used as a solo register.
Possible designs are:
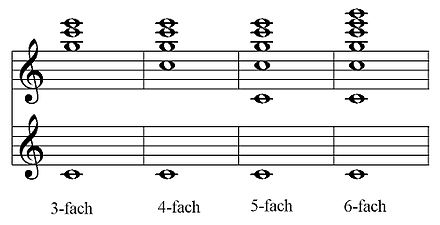
|
A cornet is called a bench and is raised behind the prospectus so that it sounds more direct. This design also saves space, since the pipes of the cornet do not have to be placed on the wind chest. This type of construction is common for French organs.
France
The cornets of the classical French organ have different names and uses:
- The Grand Cornet in the main plant has a wider bore than the others. It is usually built from c 1 (two octaves) and is mainly used to reinforce the reeds that are becoming weaker in the treble in the Grand Jeux . In the lower area this cornet is voiced a little weaker so that the transition is smooth.
- The positive cornet also serves to support the reed voices and is usually only built if such is available. It is similar to the one on the main work, only with a somewhat narrower bore overall.
- The Cornet de Récit is a solo register that is placed on the third or fourth manual. It has a larger range (from F or at least G) and is consistently strongly voiced (i.e. stronger in the bass than in the other works). A distinction is to be made between the high banked construction of the Silbermann family in Alsace and with Karl Joseph Riepp in Swabia on a common drawer of main and solo manual, which is narrower and less loud in the treble.
- The Cornet d'Écho ( Echokornett ) is similar to that of the Récit, it is often in the Echowerk or individually, mostly in a wooden box, so that the sound is muffled.
The above classification applies to large organs. In small instruments there is usually only one cornet 8 ′ 5f. in the main work (only treble). In the second manual there is usually the possibility of putting together a cornet mixture from individual registers. This so-called cornet décomposé consists of Bourdon 8 ′, Prestant 4 ′, Nasard 2 2 ⁄ 3 ′, Quarte de Nasard (fourth above Nasard = 2 ′) and Tierce ( 1 3 ⁄ 5 ′). Such a cornet is called a disassembled cornet in German and includes a full sesquialtera . It comprises at least the three individual registers ( 2 2 ⁄ 3 ', 2' and 1 3 ⁄ 5 '), which together can form a cornet within a work. In modern organs and especially outside of France, cornets other than the above Cornet d'Écho are sometimes used for echo purposes and are accordingly referred to as echo cornets.
Spain
There are also different variants in Spain.
Other variants
- Cornet registers with seventh, ninth and undecimals have been documented since the middle of the 19th century. The seventh cornet is a cornet with an additional seventh chorus 1 1 ⁄ 7 ′ or 2 2 ⁄ 7 ′. It is usually 4 or 5 times in manual work, but also 7 times with 8 ′ + 4 ′ + 2 2 ⁄ 3 ′ + 2 ′ + 1 3 ⁄ 5 ′ + 1 1 ⁄ 3 ′ + 1 1 ⁄ 7 ′ or 8-fold, in the pedals 3 or 4-fold.
- The bass zinc (also bass sesquialtera ) is a cornet-like register in the pedal, which is usually triple occupied:
|
See also
literature
- Roland Eberlein : Organ register. Their names and their history . 3. Edition. Siebenquart, Cologne 2016, ISBN 978-3-941224-00-1 , p. 131-135 .