Deptford Power Station
| Deptford Power Station | |||
|---|---|---|---|
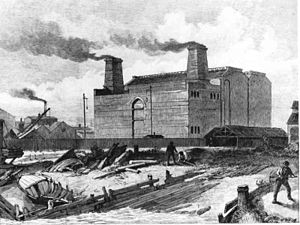
| Deptford East Power Station, circa 1890 | |||
| location | |||
|
|
|||
| Coordinates | 51 ° 28 ′ 57 ″ N , 0 ° 1 ′ 13 ″ W | ||
| country |
|
||
| Data | |||
| Type | Steam power plant | ||
| Primary energy | Fossil energy | ||
| fuel | coal | ||
| power |
|
||
| operator |
|
||
| Project start | 1887 | ||
| Start of operations | 1891 (Deptford East) 1929 (Deptford West) |
||
| Shutdown | 1957 (Deptford East) 1983 (Deptford West) |
||
The Deptford Power Station ( English Deptford power station was) a coal power plant in London's City district London Borough of Lewisham in the district of Deptford . The power plant was located on the south bank of the Thames and was characterized by two power plant units, the older part Deptford East and the newer part Deptford West .
Deptford East
The older part of the Deptford East power plant was planned and dimensioned by Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti for the London Electric Supply Corporation . When it went into operation, it was the first power plant in the world to work with a stepped-up AC voltage of 10 kV . The machinery consisted of two steam engines with an output of 7.35 MW each. The power plant delivered a maximum of 800 kW of electrical power via generators built by Ferranti.
During switching tests on the high-voltage connecting line from the power station to the center of London, Ferranti discovered the Ferranti effect , which is named after him , a voltage increase in overhead lines that are open at the end. The operation with high voltage was necessary in order to be able to bridge the distance between the power station and the electricity consumers in the city center of London economically. At that time, the electrical devices were primarily new electrical lighting devices in the form of incandescent lamps and various electric motors as drive machines . The supply in the urban area was carried out via several transformer stations with rectifiers and a lower direct voltage of around 110 V. The low-voltage networks at that time were implemented as direct current networks like Edison's for reasons of compatibility .
The plant was in operation with various modifications and improvements until 1957.
Deptford West
The Deptford West power station, which was built almost 40 years later in 1929, was originally planned by Leonard Pearce and the technical equipment was modernized in 1953. When completed, the plant had an installed capacity of 158 MW and was shut down in 1983.
literature
- Thomas P. Hughes: Networks of Power: Electrification in Western Society, 1880-1930. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore 1983, ISBN 0-8018-4614-5 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Ferranti Timeline. (No longer available online.) Museum of Science and Industry, Manchester, archived from the original on October 3, 2015 ; Retrieved July 17, 2014 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Ferranti's Deptford Power Station. Histelec News, archived from the original on June 11, 2008 ; Retrieved July 17, 2014 .
- ^ JF Wilson: Ferranti and the British Electrical Industry, 1864-1930 . Manchester University Press, 1988, ISBN 0-7190-2369-6 .
- ^ Coal-fired Power Stations. Retrieved July 17, 2014 .