Ulnar paralysis
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| G56.2 | Ulnar nerve lesion |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The ulnar nerve palsy ( Ulnarisparese ) is an injury to the ulnar nerve . It is the most common peripheral nerve damage in humans. It leads to the so-called " claw hand " or " claw hand ", sometimes also called " cyclist paralysis ".
Symptoms
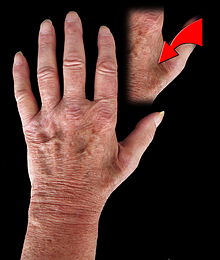
The paralysis is determined by the failure of the motor functions of the muscles supplied by the ulnar nerve. It arises from the lack of innervation in the short finger muscles. The thumb is spread apart (failure of the adductor pollicis muscle ) and when the fingers are flexed, the metacarpophalangeal joint is stretched ( lumbrical and interosseous muscles fail , since the long finger flexors are only able to bend the end joints). This results in a negative thumb-little finger sample .
Damage to the sensitive nerve part becomes noticeable through numbness in the little finger, on the outward-facing side of the ring finger and on the ball of the little finger.
The most common location of ulnar nerve damage is damage to the nerve in the area of the elbow. It is usually caused by a dislocation or fracture in the elbow joint, because the ulnar nerve runs through the ulnar sulcus . Most of the time, the damage site is at the point where the nerve enters the muscle box on the forearm. The distinction to ulnar groove syndrome ( sulcus ulnaris syndrome ) in the narrower sense is usually not made in everyday clinical practice and the cubital tunnel syndrome, factually incorrect, is referred to as sulcus ulnaris syndrome.
The direct mechanical damage in the area of the elbow, where the nerve runs directly on the “musician's bone”, is not infrequently the actual ulnar channel syndrome.
Another frequent damage site is on the wrist on the side of the little finger in the area of the so-called Loge de Guyon ( Loge de Guyon syndrome ). If the nerve is damaged at this point, depending on the exact location of the damage, only part of its hand functions are affected, because this is where the division into ramus profundus and ramus superficialis takes place .
Differential diagnosis
Similar sensory disorders and paralysis like damage to the ulnar nerve can be caused by nerve root damage to the 8th cervical nerve root, by damage to the lower arm nerve plexus ( plexus brachialis ) or by damage to the spinal cord , for example by narrowing the spinal canal . Occasionally, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis such as ulnar paralysis begins .
literature
- Marco Mumenthaler , Hans Schliack, Manfred Stöhr: Lesions of peripheral nerves and radicular syndromes. 7., completely reworked. and exp. Edition. Thieme-Verlag, Stuttgart 1998, ISBN 3-13-380207-0 .