Rotary piston pump
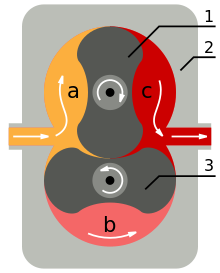
intermeshed rotary lobes (1,3) in the housing (2) a: fluid inlet, b: transport, c: outlet
Rotary piston pumps are positive displacement pumps . In the functional sketch, the pumped medium (c) is being pressed out of the pump by the rotating piston at the moment shown. If the pistons continue to rotate, will
- the pumped medium is conveyed from the divided chamber (b) to the outlet
- pending fluid (a) separated from the inlet by the first rotary piston
- and then conveyed to the outlet above this piston.
The two curved rotary pistons run without contact in cylindrical, dead space-free chambers of the pump housing.
The shear forces acting on the pumped medium are low in this design. This results in a gentle, low-pulsation conveyance of low to high viscosity media, including those with solids (e.g. unshredded fruit).
In pumps for the food industry, the interior of the pump and all parts that come into contact with the pumped liquid are usually designed in such a way that they can be cleaned residue-free by means of continuous flushing without dismantling ( CIP cleaning ).
