Income tax (Germany)
In Germany, income tax refers to the portion of income tax that is levied on income from non-self-employed work as a deduction from wages , provided that the wages are paid by an employer ( Section 38 (1 ) sentence 1 EStG ). The remaining part of the income tax revenue is called “assessed income tax”. The direct wage tax deduction was introduced in 1920 in the Weimar Republic as part of the Erzberger reform .
The employer calculates the amount of wage tax according to the information in the electronic wage tax deduction features (previously wage tax card ). In the case of annual income tax adjustment by the employer, the annual tax amount is calculated and offset in such a way that it corresponds to the annual income tax for the annual wages .
General
The employee is liable for the income tax . However, the employer must calculate the wage tax on every payroll ( Section 38 (3) EStG ), withhold it from the gross wage and pay it to the responsible tax office ( Section 41a EStG ). The employer is liable for the correct withholding and payment of wage tax and can be claimed for too little withheld and paid wage tax ( Section 42d EStG ).
The withheld tax will be offset against the income tax as an advance tax payment in the event of a later income tax assessment.
By means of the wage tax brackets are already certain the PAYE personal characteristics such as marital status and allowances into account, resulting from the income tax law arise. A basic tax allowance of 9,168 euros ( Section 32a of the Income Tax Act ) applies in the 2019 assessment period . Furthermore, since 2011, income from employment has been subject to a flat-rate amount of € 1,000 for income- related expenses ( Section 9a sentence 1 EStG ), a gross wage-related pension lump sum and a lump sum for other special expenses of € 36 ( Section 10c EStG ).
- Example tax class I or IV for 2018
30.000 € Bruttoarbeitslohn (jährlich)
— 1.000 € Arbeitnehmerpauschale (Werbungskosten)
— 4.822 € Vorsorgepauschale (bruttolohnabhängig)
— 36 € Sonderausgabenpauschale
= 24.142 € Zu versteuerndes Einkommen
Darauf wird der Einkommensteuertarif angewendet, der den
Grundfreibetrag von 9.168 € automatisch berücksichtigt.
Damit ergeben sich:
3.587,00 € Lohnsteuer (jährlich)
197,28 € Solidaritätszuschlag (jährlich)
If the employee with tax class I or IV only earns income from non-self-employed work and does not deduct any income-related expenses , special expenses or extraordinary burdens beyond the flat rates, the withheld wage tax corresponds to income tax.
Income tax registration
In addition to church tax and the solidarity surcharge , the wage tax withheld by the employer must be reported to and paid by the employer no later than the tenth day after the end of the registration period. In the course of self- assessment, the taxpayer must calculate the income tax, submit the income tax declaration on the officially prescribed form and pay the income tax. Since January 2005, income tax notifications have to be sent electronically ( ELSTER ) to the tax offices.
The registration period is generally the calendar month. Amounts the payable income tax for the previous calendar year
- more than € 1080 (from January 1, 2015, before € 1000), but not more than € 5000 (from January 1, 2017, before € 4000), the registration period is the calendar quarter,
- no more than € 1080, the registration period is the calendar year.
Income tax revenue
The cash tax revenues developed progressively. Of the wage tax revenue, 42.5 percent go to the federal government, 42.5 percent to the federal states and 15 percent to the municipalities. In 2018, wage tax accounted for 26.28 percent of total tax revenue in Germany and was thus ahead of sales tax (22.60 percent). In the previous year, the share of total tax revenue was 26.57 percent.
| year | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| amount | 132.190 | 133.090 | 123.895 | 118.919 | 122.612 | 131.773 | 141.895 | 135.165 | 127.904 | 139.749 | 149.065 | 158.198 | 167.983 | 178.890 | 184.826 | 195.523 | 208.231 |
National accounts
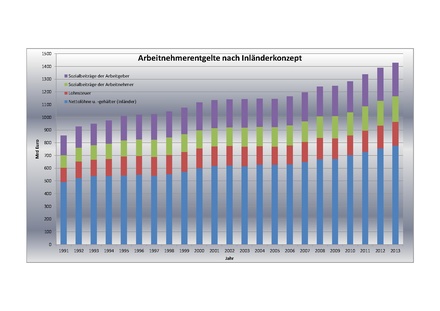
In the national accounts , the wage tax, together with the employees' social contributions, forms the difference between gross and net wages and salaries.
See also
Web links
- Wage and income tax calculator of the Federal Ministry of Finance
- Income tax calculator with representation of the calculation method
- Payroll tax for Excel
- cash tax revenues
Individual evidence
- ↑ § 41a EStG - single standard. Retrieved November 10, 2017 .
- ↑ For the tax revenue 2012-2014: for example online here . Retrieved November 14, 2015.
- ↑ a b Statistical Yearbook 2019 - Chapter 9: Finances and Taxes. (PDF) In: Federal Statistical Office . October 30, 2019, accessed on November 9, 2019 (p. 281, years 2015-2018).