Local oscillator
A local oscillator or local oscillator ( LO for short ) is the name of an oscillator that generates an auxiliary frequency . With his help with a mixer , the transmit or receive frequency changed, it creates the intermediate frequency , short- IF or IF for English frequency intermediates .
application
Local oscillators are used in communications engineering and laser spectroscopy, among other things . In laser spectroscopic measurements, laser beams , i.e. electromagnetic waves , serve as local oscillators.
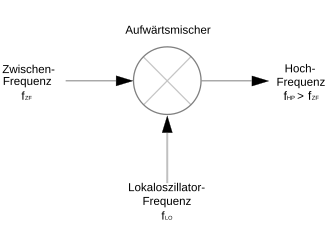
The main application is the heterodyne receiver , in which the receiving frequency is converted to a lower, constant (and easier to process) intermediate frequency (IF). The required frequency of the LO can easily be calculated:
- LO = RF - ZF or LO = RF + ZF, with RF = transmission or reception frequency.
The LO frequency is usually with the aid of quartz oscillators or VCOs ( English voltage controlled oscillator , by the phase-locked loops are stabilized (PLL)) is generated. Unstable oscillators such as the three-point circuit are also used in simple devices .
example
Intermediate frequency 90 MHz, desired transmission frequency 1.8 GHz
- LO = 1.80 GHz - 90 MHz = 1.71 GHz
or
- LO = 1.80 GHz + 90 MHz = 1.89 GHz
literature
- Thomas Mühl: Introduction to electrical measurement technology . 4th edition, Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, Wiesbaden 2014, ISBN 978-3-8348-0899-8 .
- Dirk Jansen: Optoelectronics . Basics - components - transmission technology - networks and bus systems, Friedrich Vieweg & Sohn Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Wiesbaden 1993, ISBN 978-3-528-04714-6 .
- Ekbert Hering, Klaus Bressler, Jürgen Gutekunst: Electronics for engineers and natural scientists. Springer Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg 2014, ISBN 978-3-642-05499-0 .
Web links
- IT knowledge local oscillator (accessed on September 8, 2017)
- Where to Use Clocks and Oscillators (accessed September 8, 2017)