Milas hydroxylation
The Milas-hydroxylation is a name reaction of organic chemistry , which goes back to Nicholas A. Milas and Sidney Sussman. The reaction was first published in 1936 as a synthesis for the production of cis diols .
Overview reaction
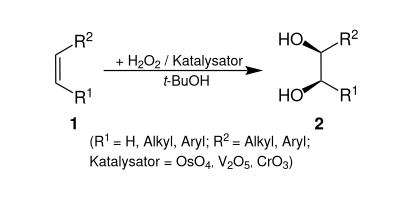
The Milas hydroxylation is an oxidation reaction between an alkene ( 1 ) and hydrogen peroxide to form a cis -diol ( 2 ) in the presence of e.g. B. catalytic amounts of osmium tetroxide (OsO 4 ) .
Reaction mechanism
A possible reaction mechanism for Milas hydroxylation is described by Zerong Wang as follows:
The hydrogen peroxide ( 1 ) forms an intermediate product ( 3 ) with the catalyst osmium tetroxide (OsO 4 ) ( 2 ), which reacts with the alkene after the rearrangement and forms another intermediate product. Subsequent cleavage of OsO 4 results in the cis diol ( 4 ).
application
Milas hydroxylation is used in preparative chemistry .
See also
Dihydroxylation , Sharpless dihydroxylation , Prévost hydroxylation