Flexor hallucis longus muscle
| Musculus flexor hallucis longus (humans) Musculus flexor digitorum lateralis (animals) |
|---|
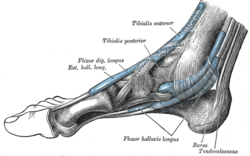
|
| Flexor hallucis longus muscle (human) |
| origin |
| Posterior surface of the fibula , interosseous membrane |
| approach |
| Terminal of the big toe Animals: Terminal of the supporting toes |
| function |
| Big toe flexor (lat. Hallux) |
| Innervation |
| Tibial nerve (branch of the sciatic nerve ) |
| Spinal segments |
| L5, S1 |
The flexor hallucis longus muscle ( Latin for "long big toe flexor ") is a skeletal muscle and one of the flexor toe muscles . It is the strongest of the deep flexors. The tendon of the muscle passes through the tarsal tunnel , crosses in the area of the sole of the foot with that of the flexor digitorum longus muscle and connects to it at this point. The flexor hallucis longus thus strengthens the effect of the flexor digitorum longus.
In domestic animals, the muscle is referred to as one of the three heads of the deep flexor toe as the flexor digitorum lateralis muscle . Here its tendon connects with those of the other two heads of the deep toe flexor ( Musculus tibialis caudalis , Musculus flexor digitorum medialis ) to form the deep flexor tendon . This then splits according to the respective number of toes and pulls on the phalanx distalis (coffin, claw or claw bone) of all supporting toes.
function
The flexor hallucis longus muscle flexes the big toe down and also helps plantar flexion (downward flexion) of the foot .
In animals, the muscle acts as an extensor of the ankle and, above all, as a flexor of the toe joints .