Myotoxin
Myotoxin (from ancient Greek μῦς mys , gen. Μυός myos 'muscle' and τοξίνη , ancient Greek pronounced toxíne 'the poisonous substance', collectively muscle poison ) is a snake poison - peptide with a muscle paralyzing and muscle-destroying function. In the venom of the rattlesnakes ( Crotalus ), in particular, there are various homologous peptides that have this function.
history
The Brazilian scientist José Moura Gonçalves purified and identified in the 1950s the first Myotoxin, Crotamin , from the venom of Neotropical rattlesnake (Crotalus durissus terrificus) , a tropical rattlesnake that in South America is home.
Structure and function
Structurally very similar myotoxins - all of them are small, basic peptides with molecular masses around 4.5 kDa, isoelectric points (pI) around 9.8 and structurally stabilized by three disulfide bridges - are present in the venom of pit vipers and vipers . The myotoxins lead to muscle paralysis ( myotoxicity ) in prey and prevent them from escaping. Death occurs within minutes through paralysis of abdominal breathing and another non-enzymatic mechanism that leads to local death of muscle tissue ( myonecrosis ).
Sequence homology
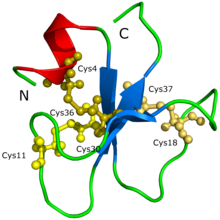
Myotoxins from various snake venoms were isolated and characterized primarily in the 1960s to 1980s. The comparison of their amino acid sequences shows a high degree of sequence homology and the conservative maintenance of the three cystines (six cysteines that form three disulfide bridges: Cys4-Cys36, Cys11-Cys30 and Cys18-Cys37), which stabilize the structure of the myosin molecule ( yellow: cysteine; green: conservatively homologous (identical) amino acid sequence):
designation |
Amino acid sequence ( single letter code ) | Species ( Crotalus ) |
|---|---|---|
| Crotamine | YK Q C HKK G GH C FPK EK I C L PPSSD F GKMD C RW R WK CC KK GSG | C. durissus terrificus |
| Myotoxin I. | YK R C HKK E GH C FPK TV I C L PPSSD F GKMD C RW K WK CC KK GSVN | C. viridis concolor |
| Myotoxin II | YK R C HKK G GH C FPK EK I C T PPSSD F GKMD C RW K WK CC KK GSVN | C. viridis concolor |
| Myotoxin II m. | YK R C HKK G GH C FPK TV I C L PPSSD F GKMD C RW R WK CC KK GSVN | C. viridis concolor |
| Peptide c | YK R C HKK G GH C FPK TV I C L PPSSD F GKMD C RW K WK CC KK SVN | C. viridis helleri |
| Myotoxin a | YK Q C HKK G GH C FPK EK I C I PPSSD L GKMD C RW K WK CC KK GSG | C. viridis viridis |
| CAM | YK R C HKK G GH C FPK TV I C L PPSSD F GKMD C RW R WK CC KK GSVNN | C. adamanteus |
Individual evidence
- ↑ G. Nicastro, L. Franzoni, C. de Chiara, AC Mancin, JR Giglio, A. Spisni Solution structure of crotamine, a Na + channel affecting toxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom (PDF; 472 kB), In: Eur J Biochem 270 (9), pp. 1969-1979 (2003). PMID 12709056 .
- ^ PR Griffin, SD Aird A new small myotoxin from the venom of the prairie rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis viridis) . In: FEBS Lett ., Vol. 274, pp. 43-47 (1990). PMID 2253781 .
- ^ Y. Samejima, Y. Aoki, D. Mebs Amino acid sequence of a myotoxin from venom of the eastern diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus) . In: Toxicon , Vol. 29, pp. 461-468 (1991). PMID 1862521 .
- ↑ V. Fadel, P. Bettendorff, T. Herrmann, WF de Azevedo Jr., EB Oliveira, T. Yamane and K. Wüthrich Automated NMR structure determination and disulfide bond identification of the myotoxin crotamine from Crotalus durissus terrificus . In: Toxicon (2005) 1; 46 (7): 759-767. PMID 16185738 .
- ↑ JC Laure The primary structure of crotamine . In: Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem (1975), Volume 246, pp. 799-803. doi : 10.1515 / bchm2.1975.356.1.213
- ↑ a b c A. L. Bieber, RH McParland and RR Becker Amino acid sequences of myotoxins from "Crotalus viridis concolor" venom . In: Toxicon (1987), Vol. 25, pp. 677-680. PMID 3629618 .
- ↑ N. Maeda and N. Tamiya Some chemical properties of the venom of the rattlesnake, "Crotalus viridis helleri" . In: Toxicon (1978), vol. 16, pp. 431-441. PMID 694946 .
- ↑ JW Fox, M. Elzinga and AT Tu Amino acid sequence and disulfide bond assignment of myotoxin a isolated from the venom of prairie rattlesnake ("Crotalus viridis viridis") . In: Biochemistry (1979), vol. 18, pp. 678-684. PMID 570412 .
- ↑ Y. Samejima, Y. Aoki and D. Mebs Structural studies on a myotoxin from "Crotalus adamanteus" venom in Progress in Venom and Toxin Research (1988), pp. 186–187, P. Gopalakkrishnakone and CK Tan (eds.) , Natl. Univ. Singapore Press, Singapore.
literature
- Alan L. Harvey (Ed.): Snake Toxins , International Encyclopedia of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Sect. 134, Pergamon Press, New York, Oxford, Beijing, Frankfurt, São Paulo, Sydney, Tokyo, Toronto 1991, pp. 70–71 (general), pp. 118–119 (mechanism), pp. 120–121 (structure / Activity); Pp. 394-395 (cloning); P. 435 (sequences).
